Analysis of the whole chain game: Is it a bubble or a new revolution? Thinking about the core advantages and business model
author:Fred@Dacongfred
Navigation Directory
This article has 13,000 words and takes about 10 to 15 minutes to read.
1. Introduction: What is the full-chain game?
2. Why do humans need full-chain games?
3. Analysis of the current status of the entire chain game industry
4. The core advantages of full-chain games
5. Challenges and limitations of full-chain games
6. Extended thinking on the full-chain game business model
VII. Conclusion
1. Introduction: What is the full-chain game?
Recently, the pass card fomo of the full-chain game Sky Strife reached 21,000 ETH, which made many non-full-chain game players begin to marvel at the magic of this track. Since the advent of "Pong" in 1972, the game industry has been soaring, from classic 8-bit games like "Super Mario" and "The Legend of Zelda" to today's highly complex and social online games such as "Fortnite" and "League of Legends". Games are no longer simple entertainment. The social, competitive and immersive experience given by these games has surpassed our imagination in the past.
However, withBlockchainThe rise of technology andcryptocurrencyWith the development of the gaming industry, we are reshaping our experience in unprecedented ways. From innovative works such as Axie Infinity that closely integrate games with the crypto economy to game projects such as Stepn that focus on social interaction and innovation,BlockchainGames are gradually being regarded as a platform for Crypto Mass Adoption, and people are gradually beginning to explore games andBlockchainIn addition to putting assets on the chain, can more elements be put on the chain? This is how the full-chain game was born.
So what is the difference between full-chain games and traditional games?
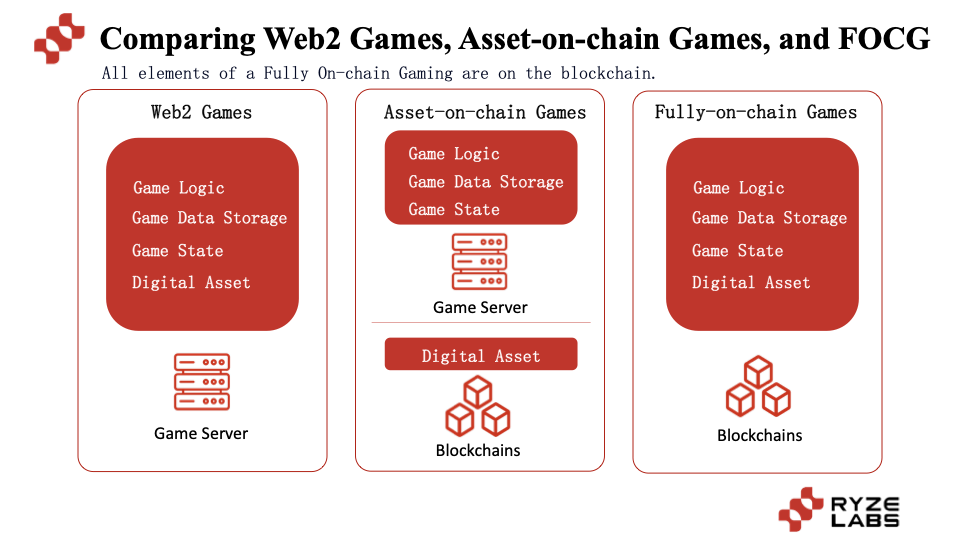
In traditional games, all our game logic, data storage, digital assets, and game status are stored in centralized game companies. For example, when we play Honor of Kings, Genshin Impact, and DNF, all game content including in-game assets are also owned by centralized companies.
The subsequent asset-on-chain games (commonly known as Web2.5 games), such as Axie and Stepn, put assets on the chain. On the one hand, players can own the assets, and on the other hand, the liquidity of assets can be improved. However, when the game is closed, the game assets will still face the dilemma of losing circulation value. The relationship between asset-on-chain games and traditional games is more like a supplement than a replacement, similar to the relationship between takeout and catering stores. Similarly, Web2.5 games are also facing competition from similar Web2.5 games and traditional Web2 games.
而最近备受关注的全链游戏将游戏所有的交互行为和状态全部上链,包括刚刚提到的游戏逻辑、数据存储、数字资产和游戏状态,全部都由Blockchain处理,从而实现真正的去中心化游戏。
To facilitate your understanding, I summarize the characteristics of the full-chain game into the following four points:
- The authenticity of the data source is ensured by the blockchain. The blockchain is no longer just an auxiliary storage of data, but the real source of game data; it is not limited to just a record of asset ownership, but a storage center for all key data. This approach fully utilizes the characteristics of programmable blockchain to achieve transparent data storage and permissionless interoperability.
- The logic and rules of the game are controlled by smartcontractFor example, various operations in the game can be performed on the chain, ensuring the traceability andSafetysex.
- 游戏开发遵循开放生态系统原则。游戏合约和可访问的游戏客户端都采用开源模式,为第三方开发者提供了广阔的创作空间。他们可以通过插件、第三方客户端和可互操作的智能合约,甚至重新部署和定制自己的游戏体验,创造性地输出内容并与整个Communityshared.
- The game has nothing to do with the client. This is closely related to the first three points, because the key to a truly crypto-native game is that even if the core developer's client disappears, the game can still continue. This depends on the permissionless storage of game data, the permissionless execution of logic, andCommunityThe ability to independently interact with the core smart contract without relying on the interface provided by the core team, thus truly achieving decentralization.
2. Why do humans need full-chain games?
Before understanding why full-chain games are needed, let us first have a brief understanding of the current situation and operation model of the traditional game industry.
Full-chain games are essentially games. Understanding the operating model of traditional games is very important and necessary for us to understand and analyze the future of full-chain games.
1. Current status of traditional game industry
With the development of the game industry, many excellent Web2 games have been born in the process of our growth, whether it is FPS such as Counter-Strike and CrossFire, or RPG such as Dungeon & Fighter and Dragon Nest, or MOBA such as League of Legends and Honor of Kings, or card such as Onmyoji and Hearthstone, games have accompanied the growth of our generation and occupied a very important part of our entertainment life.
According to data from Fortune Business Insights, the global game market size will be $249.55 billion in 2022, and is expected to exceed $280 billion in 2023 and exceed $600 billion by 2030. Compared with the film and entertainment industry, the global market size will be $94.4 billion in 2022. It can be seen that as a cultural and leisure industry, games occupy a very important position in economic development. There are many areas worth exploring in the depth of commercialization and the breadth of types. It can be said to be the crown of the leisure industry.
1) Why do humans love to play games?
According to statista data, the number of game players in the world has exceeded 2.5 billion, approaching 3 billion. So how can games attract more than one-third of the world's population to participate? The core reason can be summarized as satisfying human needs and weaknesses in many ways:

- Escape from reality and restart life: Games provide a place to escape the stress and challenges of daily life. In games, people can get rid of the troubles of reality, immerse themselves in the virtual world and have a second life.
- Socializing without burden: For multiplayer online games, the game provides a platform for social interaction and is relatively friendly to people with social phobia. Players do not have to worry about the eyes of others in real life, so they can do what they want and build relationships with others.
- Get rewards for timely feedback: Unlike students and workers in real life who struggle day after day with their studies and work, the fascinating thing about games is that they provide a rich reward system and a timely reward mechanism. After making efforts, defeating monsters and leveling up, and completing challenges, you will soon gain new skills, unlock new levels, or get new items. This incentive mechanism can motivate people to keep moving forward.
- Low-cost free exploration: Many games provide rich virtual worlds, allowing players to explore unknown areas, interact with NPCs and other players, and promote the development of the plot, which satisfies the human desire for adventure and exploration. In the real world, due to the constraints of money, energy, time and geographical location, the cost of exploration in the game world is much higher.
- Pursuit of achievement and self-realization: By completing a series of tasks and goals, people can realize their desire for success and recognition. Whether it is the leaderboard or achievement value, people can more easily achieve self-challenge and character growth in the game.
By targeting one or more human weaknesses, games can cleverly meet the needs and preferences of different users, making them play a good role both in covering a wide range of people and providing a deep immersive experience.
2) Current status and development of traditional games
Next, let us take a brief look at the current situation of the traditional gaming industry.
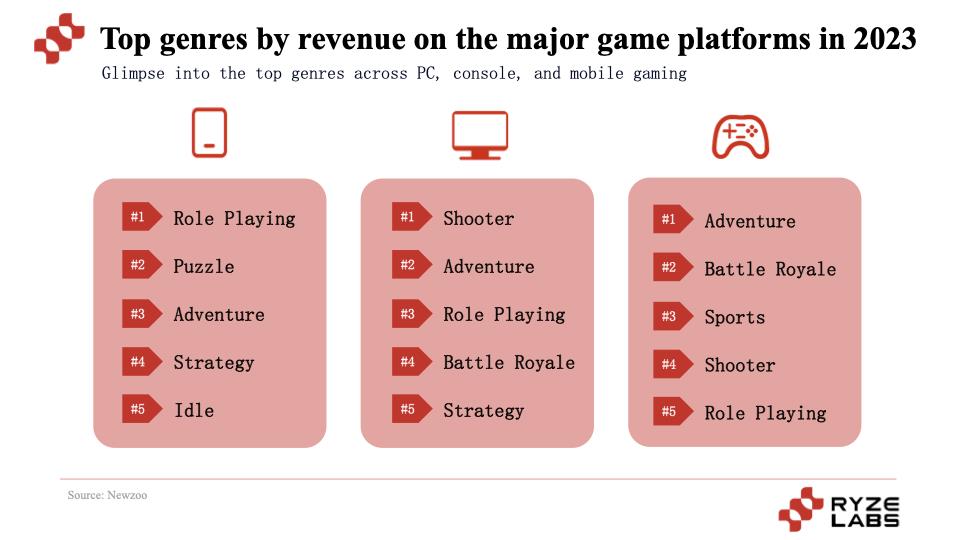
In traditional games, they are roughly divided into Shooter, Adventure, Role Playing, Battle Royale, Strategy, Sports, Puzzle, Action, Simulation and other game types.
According to Newzoo's data, role-playing and adventure games performed well on PC, mobile and consoles, ranking in the top five. In addition, shooting and battle royale games are very popular on both PC and consoles. What is slightly different on mobile is that puzzle and placement games are also popular among users.
2. Dilemma of the traditional gaming industry
However, traditional games currently face two biggest difficulties: first, game distribution is restricted by publishing licenses; second, the cost before game release is too high, resulting in a slow payback period and prone to silent costs.
1) Game distribution is subject to version number restrictions
Game version number refers to a specific license issued by the government that is required to publish games in some countries or regions. This system is designed to regulate game content and ensure that games comply with national or regional laws, culture and values to protect minors from inappropriate content and maintain social stability.
For example, Germany has stricter review of game content, with particular attention paid to content that may have a negative impact on teenagers; South Korea and Japan have game rating systems, which are evaluated and issued by relevant national agencies.
In China, the impact of game licenses is even greater. China has a strict game license system, which is issued by the State Administration of Radio, Film and Television. Games need to obtain a license before they can be released in the Chinese market.
After 87 game licenses were issued on July 22, 2021, the market fell into a stagnation phase for a long time, and it was not until April 2022 that it gradually began to turn around. In April 2022, 45 game licenses were issued, and another batch of game licenses were announced in September and December. However, from mid-2021 to April 2022, only a few large companies survived the stagnation of game license approval, and a large number of small and medium-sized game companies faced bankruptcy. According to data from Tianyancha App, more than 14,000 small and medium-sized game companies (with registered capital of less than 10 million) were deregistered from July to December 2021.
China is the world's largest game market, with more than 500 million people playing video games. The game license has become a pain for countless Chinese companies. Even if the game license is resumed, the contraction or constant adjustment of the game license has become the sword of Damocles for every game project. In the days when the game license is not issued, you can hear the sighs of countless projects without capital chains facing bankruptcy.
2) The pre-issuance costs are too high and are likely to generate a lot of silent costs.
In the Web2 game development model, the initial human resources and infrastructure costs need to be borne during the game development stage, and there are idle time costs while waiting for the version number. Only when the version number is released, the game is distributed, and commercial profits are generated, can profits be shared.
It is not difficult to find that a large amount of costs are spent in the pre-production stage. Once problems arise in the development stage, the version number stage, and the user acquisition stage, all the previous costs become sunk costs. For a medium-sized game, the cost is generally in the millions of dollars. The long period of development and distribution in the early stage makes the profit cycle very long, resulting in a higher risk of obtaining expected returns.
3. Web2.5 games’ breakthrough attempt
Faced with these two difficulties, Web2.5 games were the first to break through. On the one hand, Web2.5 games bypassed the restrictions of domestic version numbers by targeting global users, and citizens of the world can play; on the other hand, by issuing NFTs and tokens, they can generate income through market making in the early stages of internal testing and start-up, thus greatly reducing the financial entry threshold for game production.
In the attempt to break through the Web2.5 game, there have emerged some very popular games such as Axie and Stepn. The popularity of Axie in Southeast Asia has led many people to use Axie tomake moneyThe income is higher than the average working income in the Philippines; Stepn's move to earn model has become so popular that many non-Web3 users have started asking, "How do you use your running shoes? I want to run, too." This has set off a wave of blockchain games breaking out of the circle. However, with the collapse of Ponzi's economic model, Web2.5 games have never sparked the same sparks as Axie and Stepn.
Builders also began to explore in different directions. Some went for AAA games to try to get a share of Web2 users. However, this led to the need for Web2.5 AAA games to compete with both Web2.5 games and Web2 games. Another group of people began to change their path and decided to turn to full-chain games to explore new possibilities and value verification. In the emerging industry of Web3, there are always people who want to be pioneers and move forward on a newer path.
3. Analysis of the current status of the entire chain game industry
At present, the entire full-chain game is in a very early stage, and both game projects and related infrastructure are under development. In the industry map of the full-chain game field, it can be roughly divided into four categories: full-chain game projects, full-chain game engines, full-chain game chains, and full-chain game distribution platforms.
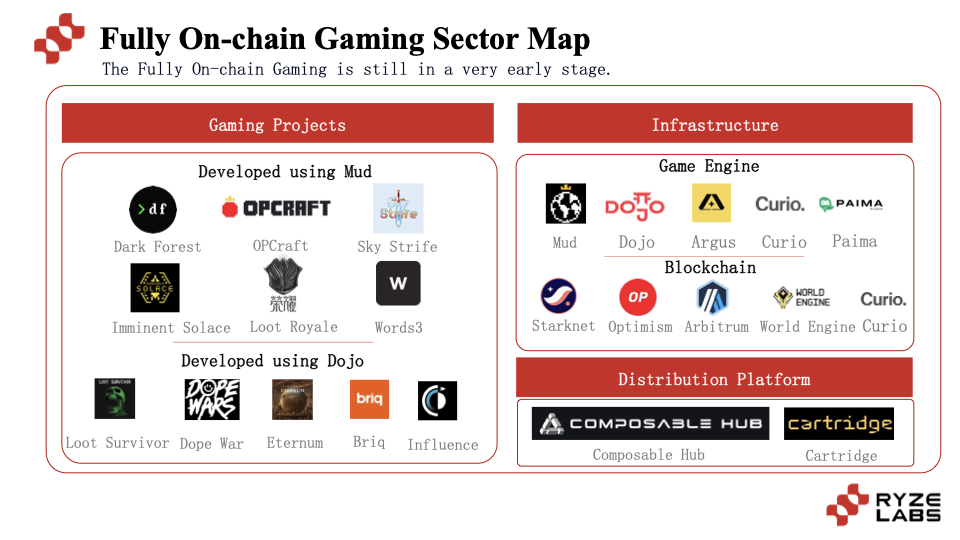
1. Full-chain game project
The current full-chain game projects are in a very early stage. Next, we will analyze several full-chain game projects to understand the current status of full-chain games.
In terms of game projects, there are the well-known Dark Forest in the early days, as well as the recent Loot survivor, Sky Strife, Imminent Solace, Loot Rayale, etc. Most of the projects that can be experienced are still in the testing stage, and the number of full-chain games that can be played on the market does not exceed two digits. The games as a whole are mainly SLG (strategy), and there are also many new project parties trying to move towards simulation management.
Since most games are still under development and unplayable, here we mainly introduce several playable and distinctive full-chain games.
1) Dark forest
First, let’s take a look at Dark Forest, a representative work of the full-chain game. Simply put, Dark Forest is a decentralized strategy game created on Ethereum using zkSNARKs.
Dark Forest was developed by MIT graduate Brian Gu under the pseudonym Gubsheep, partly inspired by Liu Cixin's science fiction novel "The Dark Forest". Other members include Alan, Ivan and Moe. This game project has not received any financing, but his team's new project Argus Labs recently raised $10 million.
Dark Forest is one of the earliest incomplete information games built on a decentralized system. As a space conquest strategy game, players explore the infinite universe by starting their journey on their own planet, discovering and occupying other planets and resources to develop their own empire.
Dark Forest has three biggest highlights: two of them were just mentioned when introducing the full-chain game. One is that the game logic, data, and status are all on the chain, and centralized individuals cannot have a single control over the results of their actions; the second is a free, open, and highly combinable game ecosystem: the open source full-chain game model gives Dark Forest permissionless interoperability. It is essentially an Ethereum smart contract that any address can interact with, giving birth to a prosperous secondary innovation ecosystem (plug-ins) and creating more ecological communities.
For example: Project Sophon wrote the Dark Forest local library, which allows users to start a game on or off the chain; the Ukrainian game organization Orden_GG built a trading market for artifacts and added a liquidity pool; DAO MarrowDAO|GuildW @marrowdao 开发了神器交易市场、GPU 开图工具在内的不少插件等,其 UGC 的生态非常的有趣。
(Source: MarrowDAO official Twitter)
Another highlight of Dark Forest is the use of zk-SNARKS technology to hide information. For strategy games, if all information is transparent, the opponent will know their position, and it will be impossible to implement strategic confrontation under full transparency. Dark Forest uses zk technology to hide most of the universe and opponents when players first enter the game. They only become visible when players explore hidden areas. Every time a player moves, a proof is sent to the blockchain to prove that the move is valid without revealing their coordinates in the universe.
Since the end of Round 5 of the official v0.6 version in February 2022, Dark Forest has not opened a new round of game versions. The entire game is currently in a free-range state. If you want to experience the game, you can participate in some rounds organized by the community, such as creating a small universe in the Arena system developed by dfDAO to experience it.
(Source: Fred created a new universe in the Arena system developed by dfDAOXiaobai Navigation)
In general, Dark Forest redefines the possibilities of Web3 games. Many people praise Dark Forest as a perfect example of the intersection between games and cryptography. It also inspires many subsequent full-chain game projects. According to previous reports, the cumulative number of players in history exceeds 10,000+.
But the significance of Dark Forest lies not only in the game itself. As the first highly-anticipated full-chain game, it is more like a spiritual totem of full-chain games, allowing industry builders to discover that based on full-chain games, there are so many free and open combinations of gameplay and a prosperous secondary innovation ecosystem that can be born, giving people stronger confidence in the possibility of realizing the "Autonomous Worlds".
And after creating Dark Forest, the Dark Forest team and several other teams formed 0xPARC. When developing full-chain games, Lattice, a sub-project of 0xPARC, found that the existing development costs were extremely high, so it started the MUD project in 2022, hoping to create a good full-chain game engine around the ECS framework to solve problems such as state synchronization between contracts and clients, continuous updating of content, and interoperability with other contracts, thereby lowering the development threshold and greatly promoting the development of full-chain games. To some extent, Dark Forest is a huge symbol and development booster for the full-chain game industry.
2) Loot survivor
Next, let’s take a look at Loot Survivor. As a game developed by the BibliothecaDAO team, Loot Survivor is an important part of the Loot ecosystem.
Loot was released by @Dom Hofmann on August 28, 2021. Unlike common PFP-type NFTs, such as BAYC and Crypto Punks, each NFT of Loot has white text on a black background, and the right to interpret these texts is very free and open. Its characteristics of being completely co-created and autonomously grown by the community have attracted a large number of ecological contributors and related derivative projects.
(Source: OpenSea)
Among them, Loot Realms has been committed to the development of Lootverse since its launch on September 1, 2021. Core contributors @lordOfAFew and @TimshelXYZ played an important role in this project and built the underlying narrative of Loot.And through Realms' first project, Eternum, the gamification of narrative is presented.
The team proposed the core "Play 2 Die" concept as early as February 2022. It was originally planned as one of the expansions of the Realms series, and the creation was called "Realms: Adventurers". However, during the iterative development process, the team decided to quickly launch a smaller single-player full-chain game, so Loot Survivor was born.
Loot Survivor is a text-based dungeon or roguelike game that made its debut at the All-Chain Game Summit in Lisbon on May 25 this year (also the author’s birthday) and attracted much attention.
The overall gameplay of the game is relatively simple. You fight monsters through text interaction until you die, and the game hopes that users will continue to challenge themselves through leaderboards.
(Source: Fred's screenshots and performance ranking on Loot Survivor)
In general, the game is smaller in size and playability. It inherits the Loot ecosystem and adds gamified narrative to the Loot ecosystem in terms of game creation. In addition, as one of the signature projects of the Dojo engine ecosystem, it also gives a boost to the Dojo engine ecosystem and the Starknet ecosystem.
3) Imminent Solace
Imminent Solace is a recently launched treasure-fighting chicken-eating game based on ZK fog of war, developed based on the Mud engine. The project team is developed by PTA DAO, a Chinese team that pays great attention to full-chain games. It combines PVP plunder, autonomous world exploration and PoW resource mining. The gameplay is similar to Dark Forest, but the operation is simpler and the user experience is higher.
The ultimate goal of the project is to create a war simulation game similar to EVE, in which players will suffer real losses in resources and assets during the game and face strategic challenges.
Imminent Solace is a relatively playable game among some of the recent full-chain games, with good game interaction and experience.
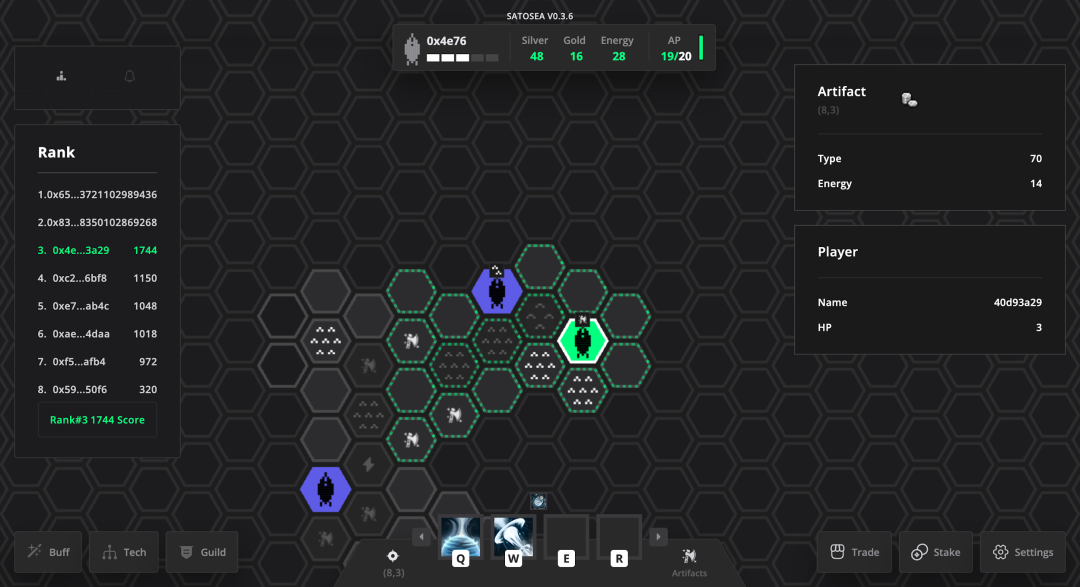
(Source: Fred's screenshots and rankings on Imminent Solace)
In addition, there are Lattice's official self-developed Sky Strife, OPCraft, SmallBrain's text game Word3, the Web3 version of Werewolf Framed, as well as the battle royale Loot Rayale, the cultivation and management Genki Cats and other games exploring the road of full-chain games. Most of them are still in the testing stage, and only a few playable games are currently being developed.
Through research, it is found that the current full-chain games are basically all Web games, with almost no PC and mobile games.
- On the one hand, this is also related to the fact that full-chain games do not require clients. Since full-chain games can have multiple front-ends, the most important thing for project owners is to quickly make an MVP version for the community and users to play. Compared with PC and mobile terminals, the web terminal has a faster development speed and lower development cost, making it the best solution or even the only choice for everyone.
- On the other hand, the full-chain game is still in the concept verification stage. How to quickly and easily create a playable game to verify the value of the game is the key.
2. Full-chain game engine
Before understanding the full-chain game engine, let’s first understand the core essence of the engine:
In simple terms, it is to see the world from the shoulders of giants. Game engines integrate some commonly used functions for making games into universal codes, so that people who want to create games later do not need to reinvent the wheel.
For example, in traditional game engines such as Unity and Unreal Engine, if game developers want to realize the movement patterns after a cosmic explosion or the movement trajectories after a collision between characters, they can directly use the existing engines and focus their energy on developing some differentiated game content.
Similarly, the full-chain game engine hopes to achieve similar goals. Compared with traditional game engines such as Unity and Unreal Engine, which can complete tasks such as graphics rendering, physical simulation, and network communication, the full-chain game engine, due to its game characteristics, pays more attention to the synchronization of the state of the contract and the client, the continuous updating of the content, and the interoperability with other contracts.
Currently, the full-chain game engines include Mud, Dojo, Argus, Curio, Paima, etc. Among them, Mud and Dojo are currently the two most mainstream full-chain game engines, which have built a situation where the EVM compatible ecosystem and the Starknet ecosystem compete for supremacy. Here we will mainly introduce these two game engines.
Mud
Mud is the first full-chain game engine officially released by Lattice in November 2022. Mud's team Lattice and the full-chain game pioneer Dark forest belong to the OxPARC team. As the earliest full-chain game engine, Mud is currently the ecosystem with the most developers. In addition to the earliest Dark Forest, projects such as OPCraft, Sky Strife, Word3, and the recent Imminent Solace were also born. It is currently the full-chain game engine with the most developers.
Dojo
Dojo was born in the Starknet ecosystem. In the early days, it was developed around MUD in the Cairo language of Starknet and was officially released in February 2023. As for why a Mud-like engine should be built on Starknet, the core developer of Dojo, tarrence.eth, said that he is enthusiastic about the Cairo language and believes that compared with the solidity language, Cairo has greater advantages in proof recursion and step-by-step proof.
But from the speech of another core developer Loaf, we can see that the reason for making another Mud-like engine on Starknet is not that Mud is not good enough, but because Loaf wants to make an ECS system on Starknet, so he chose to fork MUD. Similarly, some other Layer1/Layer2 recently wanted to develop their own full-chain game ecosystem, such as Move and Flow, and also began to fork their own engines. In essence, it is also to prosper the ecology on the chain, and choose the infrastructure of the builder full-chain game.
The Dojo ecosystem project is backed by the big IP of the Loot ecosystem, and many good projects have emerged. The Loot Survivor mentioned above is one of them, and Loot Realms: Eternum also belongs to the Loot ecosystem. In addition, there are some other projects, such as Dope Wars and Influence, which have also performed well.
Just as traditional game engines have played an important role in promoting the development of the game industry, the rise of full-chain games is closely related to the emergence of full-chain game engines, which allow developers to create game works at a lower cost. The emergence of Mud and Dojo has promoted the development of the entire full-chain game track. In May, June and July of this year, there were hackathons such as ETH AW, Pragma Cario 1.0, and Lambda zkWeek, which continuously nourished the development of full-chain games.
3. Full-chain game chain
In the field of game-specific chains, compared to the game-specific chains that have received much attention in previous Web2.5 games (not listed one by one), current full-chain game project parties prefer to build on some general Layer2 such as Arbitrum Nova, Optimism, Starknet, etc.
The fundamental reason is that the user profiles of these previous games that have switched to blockchains are all players who love to play Web2.5 blockchain games and AAA-like masterpieces. Such players are not very interested in the relatively simple and rough content of full-chain games. Therefore, these so-called game-specific chains are not very attractive to full-chain games.
In addition, it is worth noting that CaptainZ once mentioned that there is a contradiction in the current practice of putting all games on the chain: the contradiction between the push-based nature of the blockchain and the loop-based nature of the game.
Many blockchains are passively triggered by events, and only when new transactions or operations occur will the state be updated. In the existing application layer, many tracks are very consistent with this framework. For example, defi In the track, when a user wants to trade two tokens in Uniswap, the transaction is executed after it is submitted. This process is event-driven. Similarly, many social platforms are also event-driven. For example, after you post a tweet on Twitter, the tweet will be published and seen by others. It is also event-driven similar to blockchain.
However, the architecture of many traditional games is based on loops (except for some turn-based games and asynchronous games such as chess and card games). The game system will actively process user input, update game status and render the game world. Each loop is called a game loop or tick. Many games will need to run dozens or even hundreds of ticks in one second to ensure the continuous progress of the game.
This will lead to a natural contradiction between the logic of the game and the current blockchain logic. Faced with this situation, some teams began to build a proprietary chain for full-chain games, which can also be called a Ticking chain.
For example, the Argus team is building a new Layer2 based on Polaris (an EVM module compatible with the Cosmos SDK), which is a ticking chain with precompiled ticking functions, called World Engine. Curio is also building a new Layer2 based on OPStack, which also has precompiled ticking functions.
Although it is still in the development stage, we are looking forward to the emergence of a new roll-up chain structure for full-chain games, which we believe will further promote the development of full-chain games.
4. Full-chain game aggregator/distribution platform
Finally, let’s introduce the aggregator/distribution platform of full-chain games, which is still in its infancy. At present, since full-chain games are still in a very early stage, there are very few full-chain games available on the market. According to data from Composable Hub, there are no more than 30 playable games, including alpha, beta and fully launched games.
Therefore, for players of full-chain games, finding full-chain games can basically only rely on word of mouth and the spread of some small circles. defi,gamefi These mature tracks have many aggregators to help users explore and choose.
Currently, there are two main platforms that specialize in full-chain game aggregators, Composable Hub and Cartridge.
Composable Hub
Composable Hub is an aggregation platform under Composablelabs that focuses on full-chain games. Composablelabs also owns the Web2.5 Gamefi aggregation platform Klick and NFT DEX Lino Swap.
Currently, Composable Hub aggregates 56 full-chain games, of which 14 have been launched, 12 are in the testing phase, and the remaining 30 are still under development.
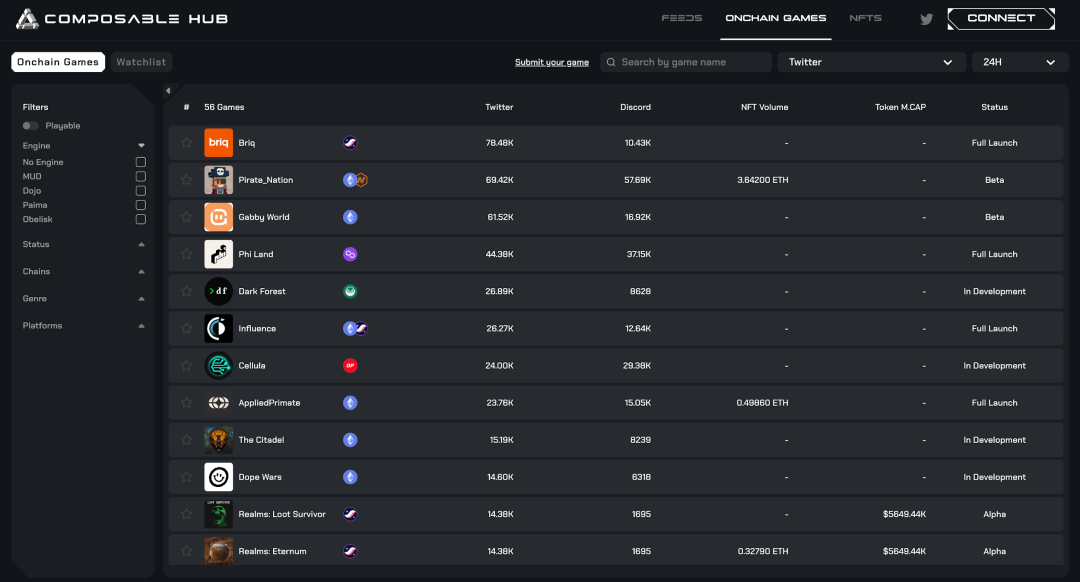
(Source: Composable Hub)
Cartridge
Cartridge is a full-chain game aggregator of the Starkware ecosystem, dedicated to building Web3 Steam. It currently aggregates 5 games from the Starknet ecosystem: Dope Wars-Roll Your Own, Influence, Loot survivor, Briq and Frens Land.
In addition, the Cartridge team has been promoting the development of the Dope Wars-Roll Your Own game and is also the core contribution team of the Dojo engine.
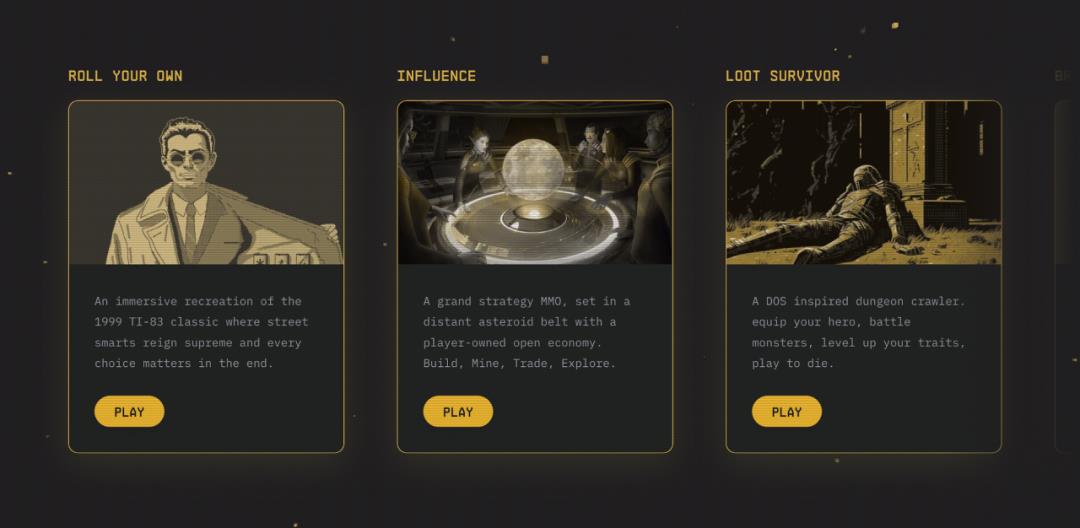
(Source: Cartridge)
4. The core advantages of full-chain games
In general, full-chain games make games fairer by putting all the game logic, status, data storage and assets on the chain. At the same time, because the game contracts and accessible game clients are open source, they provide third-party developers with a broad space for autonomy, allowing the game to have more rules and gameplay developed by the community and third parties.
This openness has transformed games from a binary division in which game companies are providers and players are consumers to a new model in which every player can become a builder and creator of the game.
1. From PGR to UGR, everyone has the right to become God
In traditional games, all our game content is provided by the official company. Whether we are playing Honor of Kings, Genshin Impact, Fortnite, or Overwatch, we are all in the PGC (Professional Generated Content) mode as game participants. Of course, we also have the right to create, and we can create some secondary creations of characters and novels around the content of the game, realizing a certain degree of UGC (User Generated Content).
However, this kind of creation does not involve the core of rules and gameplay. We can only be consumers of game rules rather than makers. We are powerless to strengthen or weaken game characters, or to affect the collision between game values and the environment. We are still within the PGR (Professional Generated Rules) specifications. For players who are eager to create, it is a kind of shackle to some extent. Frustrated humans in the real world always desire to have the right to become God, and desire UGR (User Generated Rules), whether they choose to resort to novels, movies, or games.
Most traditional games are based on business models,SafetyDue to concerns about the game's openness and stability, some developers are reluctant to make open attempts. However, we can find in many games that some projects are beginning to transform towards openness and PGR, using modules to allow other developers to develop game content outside the official scope. The most well-known example is Minecraft, which allows players to create and run their own game servers. Third-party developers can implement customized game modes, rules, and content to create gameplay that is different from the original game, including the Minecraft version of Chicken Dinner and even online graduation ceremonies during the epidemic.
Although Minecraft allows users to create multiple servers to create game modes, these new servers are separated from each other and are not connected. These different servers need to compete for players' energy and time. The data accumulated by players in this gameplay cannot be circulated in the servers of the new gameplay. This kind of UGR is castrated and is its own small universe, not a universe shared by everyone.
The creation of new gameplay in Minecraft requires the construction of new servers, while the difference of full-chain games is that they share the same backend. The interaction between different modules and smart contracts only affects the frontend, allowing data to be shared and circulated among different clients.
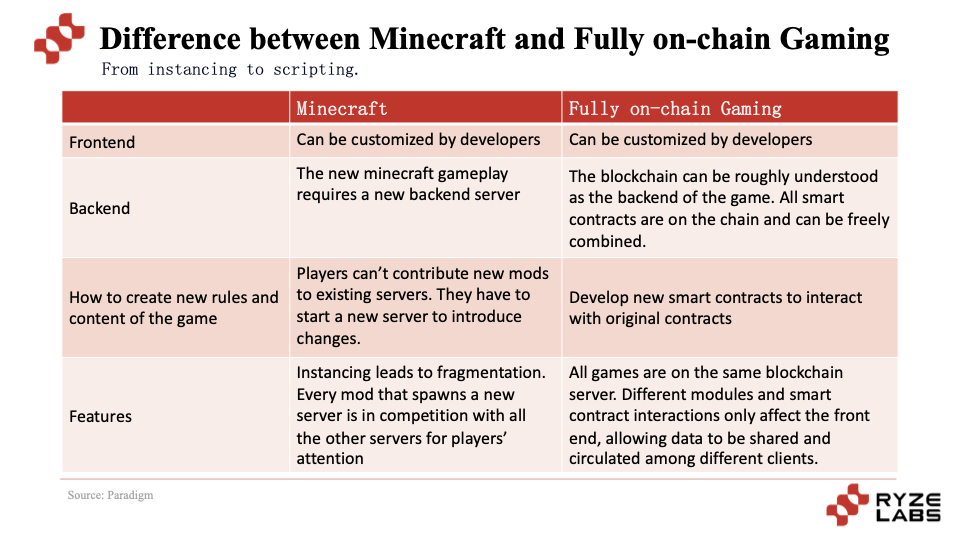
Due to the characteristics of the game logic and rules of the full-chain game on the chain and support for permissionless interoperability, players can freely build and create various game functions and experiences, and they are not isolated from each other. This possibility of free creation has greatly enriched the content and functions of the game, such as trading markets, embedded games, custom clients, etc., making the game experience more diversified and realizing the transition from PGR to UGR.
This also reminds me of the virtual world Jiuzhou created collectively by Chinese online writers Jiang Nan, Jin Hezai, Da Jiao and others more than ten years ago. They created a Jiuzhou universe through a collective relay method, forming a huge world from literary works to film and television, games and other industries.
In fact, from the analogy of our lives, full-chain games are also very similar to playing cards. Poker cards themselves only have fixed colors and numbers, but people have developed various ways to play, such as Landlord, Texas Hold'em, Tractor, Upgrade, Heart Panic, and Golden Flower, which show the diversity and flexibility of game rules. The same is true for full-chain games. By supporting open creation and interoperability, players can build a variety of different game experiences based on basic rules. In traditional games, everyone can only be a consumer of the game, but in full-chain games, people can become the makers of game rules.
To sum up, the advantage of full-chain games lies in their openness and permissiveness, which gives players greater creativity and freedom, allowing them to participate in the creation of game rules and content, thus forming a diverse, personalized and vibrant gaming ecosystem.
2. Fairness and transparency, experience a gaming environment that is not manipulated
Another major advantage of full-chain games is the transparency of their game logic and rules after they are all uploaded to the chain.
Especially for gaming and gambling games, fairness and transparency are critical.
Just like in the popular movie "All or Nothing", the gambling apps used by players are controlled by centralized companies, and all the results may not be random, but have already been written. For gambling card games such as Depp and Golden Flower, the opacity of the game process and game status will cause countless players to become big enemies, which is also one of the reasons why many Web2 gambling games with money are widely criticized.
The transparency of the game logic and rules of the full-chain game after they are all on the chain can ensure the openness and transparency of the rules. Combined with some encryption technologies (such as fog of war games Dark Forest and Imminent Solace combined with ZK-SNARK), game types that have a strong demand for game fairness can get an experience on the full-chain game that is difficult to achieve in Web2 and Web2.5 games.
5. Challenges and limitations of full-chain games
With the continuous improvement of infrastructure, the wind of full-chain games has begun to blow. However, although full-chain games have some unique highlights, there are still many limitations and challenges to be faced:
1. Poor user experience
In general, there is a consensus among players of full-chain games that the playability of current full-chain games is generally much worse than that of Web2 and Web2.5 games. On the one hand, the graphics of most current full-chain games are relatively primitive or rough, and on the other hand, there are also the following four difficulties in the interactive experience:
1) Difficulty in the beginning: It is difficult to match with other players
For multiplayer PVP games, it usually takes 4 people to play together, but since the number of players in the current full-chain games is generally very small, the number of people online at the same time is often no more than single digits. In addition, there is no matching mechanism, and many multiplayer games can only open rooms and invite people to play by themselves, which makes it easy to lose interest in the game at the beginning of the game.
2) Halal or non-halal: Some games have high artificial thresholds
In addition to the gaming experience, many games also set many artificial thresholds. For example, some games can only be played at fixed times, and some games require an entry fee before playing, such as buying certain tokens or NFTs before playing, thereby limiting and increasing the gaming costs for players.
Some game developers will maintain the spirit of independent game developers and believe that paying for games is the most pure belief. However, Web2 independent games at least have some independent innovative gameplay or high-quality content to attract players.
However, facing the current situation where most full-chain games have such low playability, why are users willing to spend money to play a game that they don’t even want to look at in Web2? To some extent, this has also reinforced the stereotype that some gamers and the outside world often have that full-chain games are just for fun. Except for a few individual project owners and believers, how many people are really willing to play? Many players are willing to play the beta version of the game just for fun, and the behavior of such project owners is somewhat discouraging for players.
3) Poor gaming experience: frequent bugs
The most important thing for players of the full-chain game is faith, followed by patience.
From PC to mobile, the development of games is generally moving towards a more convenient way.
In full-chain games, a common scenario is that several players make an appointment to play full-chain games together, and find that most of the time they will encounter bugs, whether it is the refresh of the page or various sudden errors. It is difficult for people without patience to complete the entire process of a full-chain game experience.
4) Much ado about nothing: A lot of narrative, but very little playability
Most of the current game projects are still in the situation where the narrative is large, but the actual playability is extremely low. Most games are harder to play than web games from more than 10 years ago. It is expected that with the addition of infrastructure and more builders, the playability of full-chain games will continue to narrow the gap with the playability of Web2 games.
2. Restrictions on game types
Due to the current imperfections of blockchain performance and infrastructure, not all game types are suitable for full-chain games.
From the current types of full-chain games, it can be seen that most of them are SLG type (strategy) games, which do not have such high requirements for real-time games. However, game types such as RPG, AVG, ACT and MOBA have high requirements for continuous and real-time status updates. If the data is stored on the chain, the current blockchain performance is still difficult to support timeliness. This type of game is not yet very suitable for full-chain games.
At present, the full-chain games are mainly divided into two development directions. One is to take the small and beautiful route, accumulating users through playable MVP versions, such as simulation management, pet cultivation, tower defense and other lightweight and playable game types; the other is to take the grand narrative and open world route, creating an imaginative ecology through some grand worldviews and cosmic narratives. However, due to the limitations of game types, it is basically limited to the above game types. How to make a game that breaks the circle like the next Axie or Stepn still requires our joint exploration.
3. Real demand or fake demand
The biggest challenge and controversy for full-chain games currently comes from whether the demand is real.
Take the two core advantages of full-chain games as an example:
1) From PGR to UGR, on the one hand, there are many Web2 open games that can achieve this, such as Minecraft. On the other hand, whether the server data needs to be circulated in different game clients also needs to be questioned. For example, whether the mounts, level 90, and flying wings in the RPG type client need to be circulated in the MOBA game, the necessity still needs to be explored.
2) Fairness and transparency are currently mainly reflected in gambling games. However, on the one hand, the number of online gamblers is far less than that of offline gamblers (120 million people will participate in online gambling in 2023, while the number of people participating in gambling worldwide is about 4.2 billion per year), and the ceiling is not high. On the other hand, for real gamblers, what they care most about is the convenience of deposits and withdrawals. Compared with fairness, people who love gambling care more about whether the exchange of funds and chips is fast and whether the experience is convenient. In the case of a significant gap in the full-chain game infrastructure, this is a great weakness of Web3 games at present.
Regarding the two biggest features of full-chain games, UGR and fairness, if some categories in the future can make good use of these two features, they may be able to meet the real needs of gamers and attract more people to participate. However, at present, there is still a long way to go.
4. Fully decentralized games may not be fun, but may cause chaos
Just like the two sides of a coin, the other side of openness is chaos. Since human nature is lazy, for players who only want to consume and not create, those who are accustomed to the traditional game PGR model still care most about the playability of the game.
It is difficult for the real game designers to hand over the game content to others because each user has different abilities and ordinary gamers may design the game from their own perspective, making it difficult to grasp the playability and balance of the game.
Should professional matters be left to professional game developers or should the rights be given to everyone? This is a realistic question that is worth exploring. How to achieve a balance between democracy and meritocracy is a difficult problem.
Therefore, for the development team of the full-chain game, it is very important to have an interesting and stable core gameplay while leaving space for players to create and extend new gameplay. It is very important to achieve a balance. Otherwise, it is easy to fall into the two extremes of the game being too centralized or too empty to attract players to participate in the creation of new gameplay.
For the full-chain game team, they need to play the role of "initial god", design the core gameplay of the game, and attract more players to jointly create and enrich the game world through reasonable incentive mechanisms.
6. Extended thinking on the full-chain game business model
Finally, let’s discuss with you the business model of full-chain games, which is a topic of great concern to both project owners and investors.
First, let’s analyze the business model of traditional games. The evolution of the business model of traditional video games has gone through several stages, and has continued to change with the development of technology, changes in the market, and the evolution of player needs:
- 1970s: Coin-Op Mechanics The earliest consumer video games can be traced back to the arcade games of the 1970s and 1980s. During this period, due to the hardware requirements for running video games, each game was placed in a separate physical device, including Pac-Man, Galaga, etc., where players inserted coins in exchange for game time or lives.
- 1980s: One-time purchase Early video games were mainly console games, sold through retail channels, and players bought physical game cartridges or discs. This was an era dominated by product sales, and players bought once and could play the game.
- Mid-1990s: Subscription renewal mechanism With the popularization of the Internet, multiplayer online games began to rise. Some game companies launched subscription services, where players need to pay a monthly fee to access the game server. A representative example is World of Warcraft.
- Mid-2000s: Advertising model + props charging The free game model emerged, in which the game itself is provided for free, but players can obtain additional props by purchasing virtual items or in-game currency. At the same time, some games adopt the advertising model to generate revenue by displaying advertisements in the game.
- Early 2010s: Props charging model With the popularity of smartphones, mobile games have become mainstream. In-app purchases have become a major profit model, and players can purchase various props in the app to unlock functions or speed up game progress.
- 2020s: Cloud gaming subscription model Recently, cloud gaming has also begun to come into people's view. Players can stream games through cloud servers without downloading and installing. At the same time, some game subscription services such as Xbox Game Pass and PlayStation Now have also begun to emerge, and players can get a range of games through subscription services.
These changes in business models reflect the video game industry's continuous adaptation and innovation to technology, market and player needs; similarly, the evolution of business models has also affected game design, development and player experience to a certain extent.
After Gamefi, from Axie to Stepn, the business models mainly include the following categories:
- In-game economic system: Most GameFi games have established their own economic system, using tokens, NFTs, and in-game assets as value media. Players can obtain virtual assets through game activities. These assets have value in the game and can be exchanged for real-world currencies. For example, in the well-known game Axie Infinity, players play the game by cultivating virtual creatures (Axies). These Axies are NFTs that players can trade, sell, and earn in the game.cryptocurrencyaward.
- Play-to-Earn model: Players earn income by participating in games, which can be in-game currency, tokens or other rewards of real value. For example, after players join some game guilds such as YGG, they can earn income by participating in games such as Axie Infinity and receive incentives and loans from YGG.
- Integration of DeFi and financial products: Some GameFi integrates DeFi elements to provide financial services such as loans, liquidity mining, and trading. Players can use DeFi products in the game to earn income or invest. For example, in Decentraland, players can buy virtual plots of land and create their own buildings. These plots of land can be used for investment or trading, and the value of some plots of land will also increase in the virtual world.
As for the full-chain games that are still in the very early stage, the project owners of the full-chain games are still exploring which business model to choose. However, judging from the characteristics of the full-chain games, the future of the full-chain games must focus on playability rather than DeFi. It is difficult for a simple Ponzi scheme to reap the long-time users.
The business model of the full-chain game should better combine its own characteristics to improve playability. The future business model can be roughly divided into three directions according to the type of game:
- For lightweight games like business simulation and pet training, you can consider using NFT+Token.TokenThe charging method is free-to-play but you have to pay to become stronger.
- For open-ended games with grand narratives: If the playability is high, you can consider setting a payment threshold and related subscription and membership models like independent games; but if the playability is generally low in the early stages, you can consider adopting a business model similar to lightweight games to attract users to play first.
- For games like chess and card games: the business model can refer to the commission method in the traditional/offline model.
However, the entire full-chain game is still in the stage of exploration and value verification, and we also look forward to more interesting models emerging and becoming the next mass doption.
VII. Conclusion
In general, the gaming industry has developed over decades from its birth to its integration with blockchain. Humans are not satisfied with being just game consumers of PGR, and they also have the desire to become creators of UGR.
Just as the birth of Dota originated from the custom map community of Warcraft III: Reign of Chaos. This map editor allowed players to create their own maps, one of which was Dota. From the earliest creation of Dota by Eul, to Guinsoo taking over the development of the game, adding new heroes, items and mechanisms, to IceFrog introducing a series of updates and improvements that improved the balance and depth of the game, while also adding more heroes, skills and tactical elements, bringing Dota widespread recognition and success, to Valve Corporation and IceFrog cooperating to launch DOTA 2, which has achieved great success worldwide.
The developers of the Warcraft map editor might not have imagined that a world-renowned game like Dota would be born later, and that MOBA games would become so wildly popular. On the road of user creation, it often takes a certain amount of time and opportunities to create new hit products.
The same is true for full-chain games. In today's pioneering era, there are still many shortcomings such as poor user experience and low playability. If you want to achieve mass adoption, you need to face the problem of attracting new users. If you want to attract more Web2 players, you can't avoid the threshold for users to enter Web3.wallet, learn to buy nft, buying tokens, etc., all have very high learning costs, and have become obstacles for all Dapps. Even through account abstraction and Web3 project built-inexchangeAlthough the difficulty of entering the game and depositing funds has been simplified, the biggest question still needs to be faced: what needs of gamers does the full-chain game solve?
Narration for the sake of narration, and chaining for the sake of chaining are like looking for nails with a hammer. How to make good use of the full-chain characteristics of UGR and fairness is a problem that every full-chain game builder cannot escape. The unique characteristics of full-chain games can not only provide fairness (for example, the non-full-chain game Fren Pet, which was just launched recently, has a daily turntable function that will gain more fairness if it is executed on the chain, which will reduce the user's impression of its "funding" to some extent), but also give the game a new journey from PGR to UGR, so that every user has the possibility of becoming God.
The development of Web3 cannot avoid the wealth-creating effect, and the essence of games cannot avoid playability. How to combine the wealth-creating effect and playability still requires further exploration. I hope that through continuous exploration in the full-chain game track, game projects that really take advantage of the full-chain characteristics and solve real needs will emerge. I also look forward to the future on the road of full-chain games, and the growth of a new universe in the ocean of openness.
Finally, I would like to express my sincere gratitude to Mr. Ni, Constance, Joven, Karvin, Yolo, Xiao Hu, Manda, Xiao Ran, Norman, Alex, Carl, Justin, frost, Haiyu, Nico, Golem, yafon, Gink, Robinn and other partners for their help, as well as everyone who was very willing to share their patience during the communication process. I sincerely hope that the builders in this track will get better and better!
The article comes from the Internet:Analysis of the whole chain game: Is it a bubble or a new revolution? Thinking about the core advantages and business model
Rollup is the best existing solution for scaling high-throughput applications, especially fully on-chain games. Written by: Mohamed Fouda Translated by: Coderworld Application Rollup is emerging as the clear winner for scaling a specific set of Ethereum applications. These applications benefit from permissionless and…