Mobile currency + Web3 = borderless, diversified, open inclusive finance?
Author: Liu Ye Jinghong, Weisman Notes
What is Mobile Money
Mobile money is not the same as mobile payment. According to the definition of the African Development Bank, mobile money is different from the money in traditional bank accounts. It refers to the money stored in the user's SIM card. The SIM card replaces the bank account number as the user's identity identification code.
Therefore, mobile money is a financial service innovation that uses information and communication technology and non-bank physical networks to extend financial services to areas and people not covered by traditional banks. It has two main characteristics: first, customers complete deposit and withdrawal operations on a network outside the banking system; second, customers complete transactions through a mobile phone interface.
Mobile money accounts work a bit like Venmo, but with one key difference: No bank account is required. To deposit or withdraw cash from the app, the mobile money system uses human agents who carry cash and cell phones and hang out at key locations around the country, including remote rural areas. Mobile money can also be used to make cashless transactions, including buying goods or paying bills.
The mobile money market
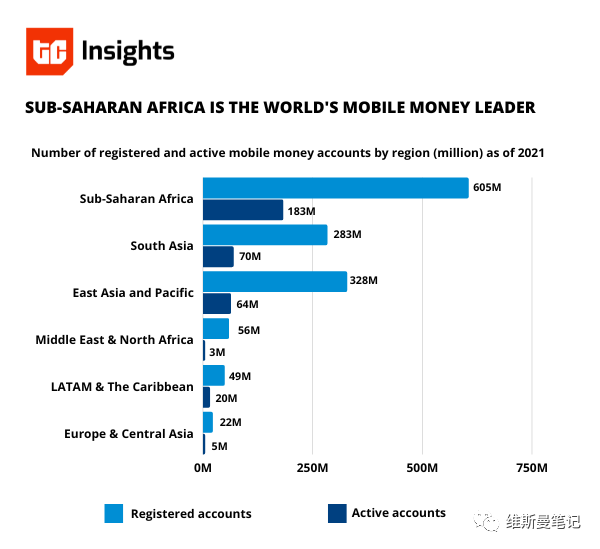
According to the 2021 report of the Global Telecommunications Manufacturers Association (GSMA), in Sub-Saharan Africa, $697.7 billion (up 40% year-on-year) was processed by mobile money options. The region also accounted for nearly 70% of the total global transaction volume (US$1 trillion) last year, far exceeding South Asia (US$156.3 billion).
Additional information from the GSMA report shows that there are already more than 184 million active mobile cash accounts in Africa.wallet, while there were only 161 million accounts more than a year ago. I believe that in 2023, the latest data will show a greater growth trend.
Why is there a need for mobile money?
In the eyes of most people, modern mobile payment, electronic currency and evencryptocurrencySo why is there a need for mobile money? There are three key reasons:
1. Low financial coverage in remote and underdeveloped areas
Globally, there are still large remote areas and underdeveloped countries, a typical example being African countries, where the financial needs of people cannot be met. According to the World Bank's 2023 annual report, only 28% of the population in African countries use the Internet, which means that more than 70% of people cannot use modern, fast and convenient financial services.
Cited from TheGlobalFindexDatabase202Xiaobai NavigationAccording to data from 1, the global personal account ownership rate is 76%, which means that there are still 24% of the world's population who do not have a personal account.
2. Traditional bank branches and ATMs have high operating costs
The operating cost of promoting traditional bank branches in remote and economically underdeveloped areas with sparse populations is high and the profit is low. If you want to use an ATM, you need to open a personal account and bank card at the branch first, which makes the problem become a question of "which comes first, the chicken or the egg". Therefore, mobile money can expand the scope and groups of financial services with less infrastructure investment, and is more inclusive.
3. Mobile banking and third-party payment have high barriers to entry
Existing mobile banks or third-party payment service providers can be operated through mobile phones, but these services require users to have a personal account and a linked bank card. For economically underdeveloped areas, there may not be traditional bank branches to handle related services.
Based on the above three points, it is clear why the seemingly backward mobile money technology is still used by many groups. Mobile money is almost the only inclusive financial service in underdeveloped and remote areas.
MTN MobileMoney Case
Before introducing Web3, I need to briefly introduce the existing mobile currency operation model.
MTN is the largest telecommunications operator in Africa. The multinational telecommunications group has operations in 22 countries in Africa and the Middle East, providing services to 219 million users. The mobile currency launched by MTN is called MTN MobileMoney, which is the most widely used mobile currency in Africa and has been promoted to East and West African countries such as Uganda, Cameroon, Ghana, Cote d'Ivoire, Rwanda, Benin, Nigeria, and Zambia.
Users can become registered users through their mobile phone numbers. After registration, they will get a mobile money account based on telecom operators. The balance of the mobile money account can be increased by depositing cash at authorized agent outlets. Users can complete remittance operations using their mobile phones, and the recipient will receive a withdrawal SMS from MTN. After the account is verified at the agent outlet, the cash can be withdrawn. Users can also store cash in their accounts and use mobile money to pay bills, purchase goods, etc. between MTN's partner institutions.
In terms of business profitability, MTN mainly relies on the fees of remittance business. When both parties are MTN mobile money users, the highest remittance fee is only US$1. Its agent outlets have no right to charge various fees and can only earn commissions from MTN after users deposit or withdraw cash.
In terms of business model, the entire MTN operating network is divided into three roles: custodian bank, super agent, and retail agent. Custodian bank is responsible for the custody of MTN customer funds, super agent is a financial institution or partner, responsible for providing mobile money and cash management and allocation to retail agents. Retail agents directly face users and assist users in using MTN mobile money and deposit and withdrawal transactions.
MTN MobileMoney flaws
Although mobile money has filled the gap in inclusive financial services in underdeveloped areas, there is still a lot of room for improvement. The shortcomings that can be seen at present include three points.
one, The process is cumbersome and highly dependent on agentsWhether it is registering an account or transferring money, depositing or withdrawing money, you need to go to a retail agent, but retail agents are not as widely distributed as 711. Without the coverage of retail agents and cooperative institutions, it is basically impossible to complete the service.
two, High maintenance costMTN currently maintains more than 20,000 retail agent outlets, and many of them rely on manual processing. The huge outlet operation costs are also one of the shortcomings in economically underdeveloped areas.
three, Only local currency is supportedCurrently, MTN only supports local currency services and a very small number of insurance financial services. In a broader sense, inclusive financial services are not perfect enough. There is no savings service such as current and fixed deposits, and no more advanced financial products.
Mobile money combined with Web3
So what can such a combination of mobile currency and Web3 bring? The advantages are still three points.
one, Permissionless Financial Inclusion Network。Web3无须开户,无须提供各种证明。可以通过SIM卡与Web3钱包地址绑定直接获取去中心化账户。并且可以直接连接Web3的开放金融世界,通过Maker DAOThere is no need for a centralized custodian to hold funds, and a high degree of trust in financial services can be achieved through open protocols.
two, Extremely low-cost decentralized ledgerUnlike the operating costs of MTN's more than 20,000 retail agent outlets, mobile money combined with Web3 can be directlyBlockchainBookkeeping is done through the Internet, and decentralized inclusive financial services are completed throughout the process. Through technologies such as Layer2, the fee rate can be compressed to far less than $1.
three, Cross-currency open financial network. Under the existing mobile currency system, only supporting payments in local currency is not enough to achieve inclusive finance. Because of underdeveloped economies and even regional financial bankruptcies (such as Greece’s bankruptcy), holding local currency is a disaster for people with low incomes. By introducing Web3 into mobile currency, people can use compliant US dollar digital currencies such as USDC to avoid the harvesting of local exchange rates. Or they can purchase RWA’s compliant assets to ensure the appreciation and preservation of their own wealth.
Web3's open finance brings borderless and more diversified inclusive financial solutions, but there are also a series of problems such as fraud, rugs, hackers, etc. These dark forests of Web3 require promoters to conduct some centralized audit screening. I never think that Web3 needs a completely unregulated and decentralized utopian world. Therefore, introducing appropriate regulatory agencies and financial institutions to assist Web3 open networks may be the future of Web3. These are my understandings of Web3 open networks, balance.
The article comes from the Internet:Mobile currency + Web3 = borderless, diversified, open inclusive finance?
本文整理介绍了本次黑客松的部分优秀作品及其核心创新点。 撰写:ETHGlobal 编译:小白导航 coderworld 最近的 ETH Global New York 黑客松展示了开发者们构建 DApp 的创造力。本文整理介绍了本次黑客松的部分优秀作品及其核心…