SharkTeam: 2023 Cryptocurrency Crime Analysis Report
Written by: SharkTeam
In 2023, the Web3 industry experienced more than 940 large and smallSafetyThe number of incidents in 2022 increased by more than 50% year-on-year, with the loss amount reaching 1.79 billion US dollars. Among them, the incidents in the third quarterSafetyThe number of incidents was the highest (360) and the losses were the highest (US$740 million), with losses increasing by 47% year-on-year in 2022. In particular, in July, there were 187 incidents.SafetyThe incident resulted in losses of US$350 million.
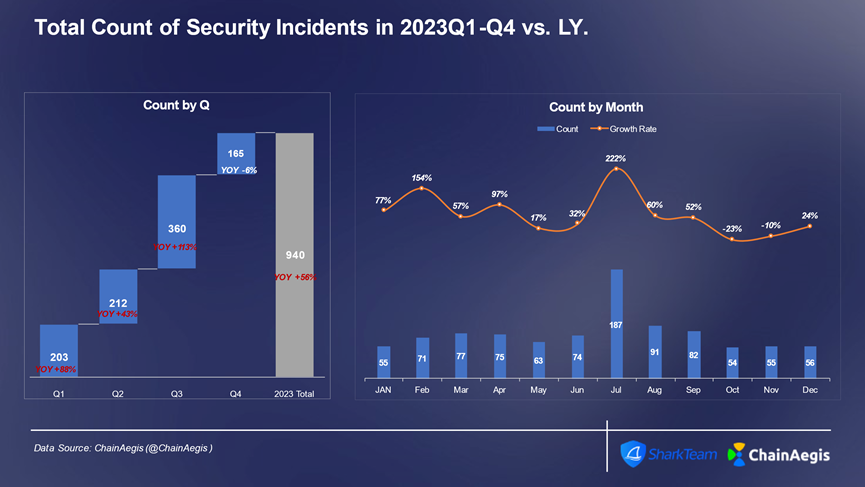
Figure: Web 3 2023 Quarterly/Monthly Security Incidents
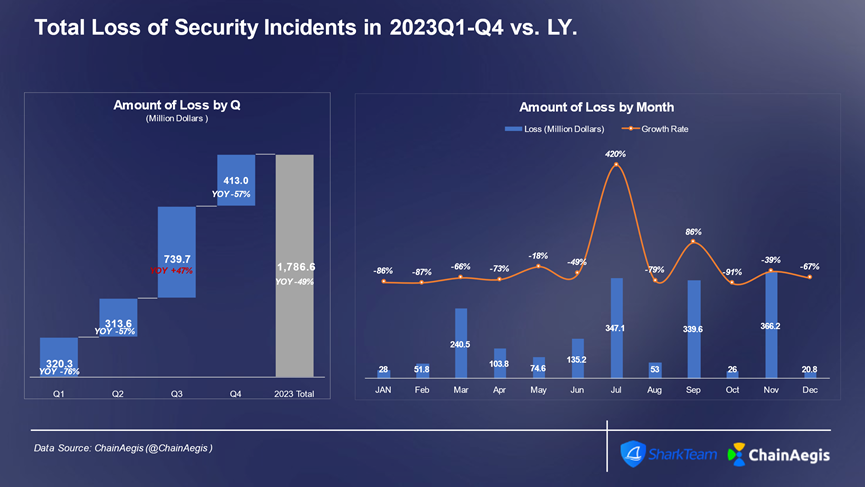
Figure: Web 3 2023 Quarterly/Monthly Security Incident Losses (US$ Million)
First, hacker attacks are still a major cause of significant losses. In 2023, there were 216 hacker attacks, resulting in losses of $1.06 billion.contractVulnerabilities, private keysstealPwning, phishing attacks, and state hackers are still the main reasons threatening the security of the Web3 ecosystem.
Secondly, Rugpull and Ponzi scheme frauds are on the rise. In 2023, there were 250 Rugpull and Scam frauds, of which BNBChain had the highest frequency. Fraudulent projects attract investors by launching seemingly attractive crypto projects and providing some false liquidity. Once they attract enough funds, they will suddenlystealWithdraw all funds and transfer assets. This type of fraud will cause serious financial losses to investors and greatly increase the difficulty for investors to choose the right project.
In addition, ransomware usescryptocurrencyCollecting ransom has also become a trend, such as Lockbit, Conti, Suncrypt and Monti.cryptocurrencyCompared with fiat currency, which is more difficult to track, it is becoming increasingly important to use on-chain analysis tools to track and locate the identities of ransomware gangs.
Finally, in these criminal activities such as cryptocurrency hacking and fraud extortion, criminals usually need to launder money through on-chain fund transfers and OTC after obtaining cryptocurrencies. Money laundering usually adopts a decentralized and centralized hybrid method.exchangeIt is the most concentrated place for money laundering, followed by on-chain currency mixing platforms.
2023 is also the year when Web3 regulation has made substantial progress, with FTX2.0 restarting and sanctionsBinance, USDT banned Hamas and other addresses, and in January 2024, SEC approved the Bitcoin spot ETF. These landmark events all represent that supervision is deeply involved in the development of Web3.
This report will systematically analyze key topics such as Web3 hacker attacks, Rugpull fraud, ransomware, cryptocurrency money laundering, Web3 regulation, etc. in 2023 to understand the security situation of the development of the cryptocurrency industry.
one,contractVulnerabilities
合约漏洞攻击主要发生在以太坊上,2023 年下半年以太坊上共发生 36 起合约漏洞攻击,损失金额超过 2 亿美元,其次是 BNBChain。攻击手段上,业务逻辑漏洞和闪电贷攻击仍是最常发生。
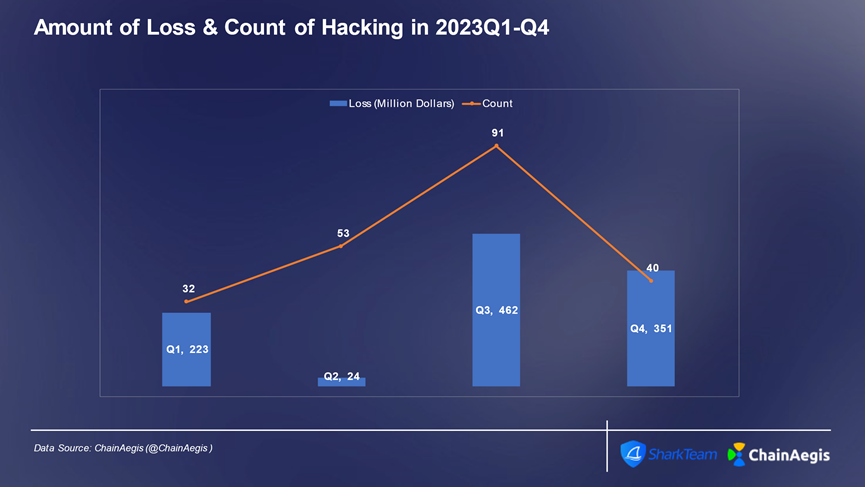
Figure: Web 3 2023 Number of hacker attacks and losses per quarter (million USD)
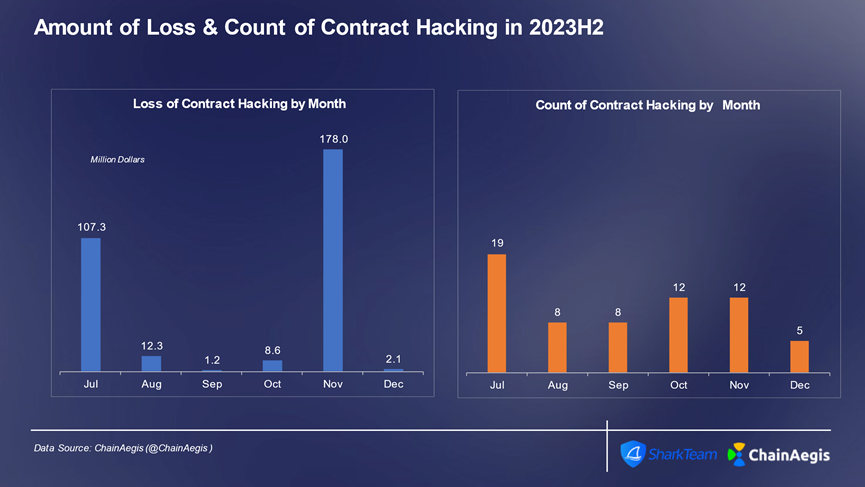
Figure: Number of hacker attacks and loss amounts of Web 3 contract vulnerability exploitation in 2023H2
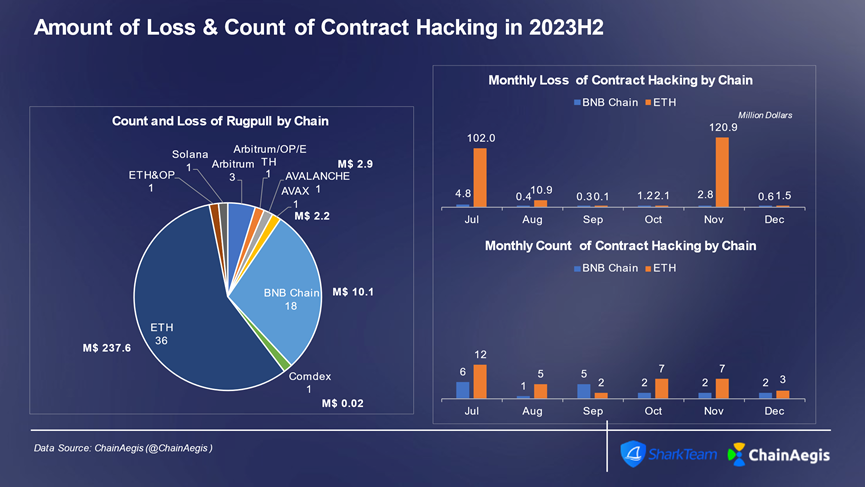
Figure: Number of contract vulnerability exploitation attacks and loss amounts on different chains per month in Web 3 2023H2
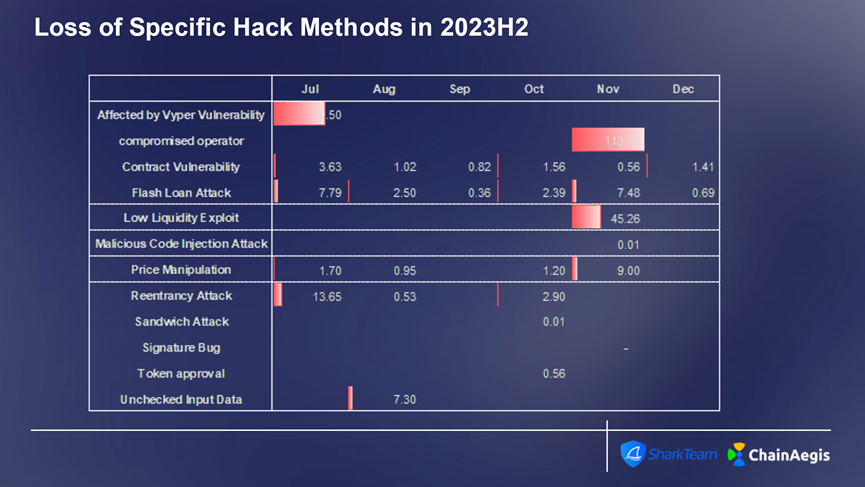
Figure: Web 3 2023H2 contract vulnerability exploitation, number of attacks and amount of loss
Typical event analysis: Vyper vulnerability leads to attacks on projects such as Curve and JPEG'd
Take the JPEG'd attack as an example:
Attacker address: 0x6ec21d1868743a44318c3c259a6d4953f9978538
Attacker contract: 0x9420F8821aB4609Ad9FA514f8D2F5344C3c0A6Ab
Attack transaction:
0xa84aa065ce61dbb1eb50ab6ae67fc31a9da50dd2c74eefd561661bfce2f1620c
(1) The attacker (0x6ec21d18) created the contract 0x466B85B4 and borrowed 80,000 WETH from [Balancer: Vault] through a flash loan.

(2) The attacker (0x6ec21d18) added 40,000 WETH to the pETH-ETH-f (0x9848482d) liquidity pool and obtained 32,431 pETH.

(3) The attacker (0x6ec21d18) then repeatedly removed liquidity from the pETH-ETH-f (0x9848482d) liquidity pool.
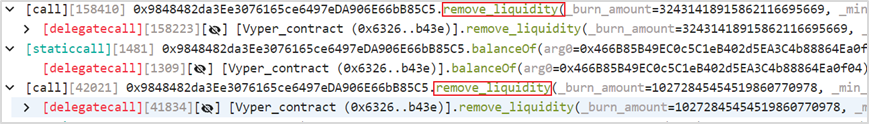
(4) In the end, the attacker (0x6ec21d18) obtained 86,106 WETH. After repaying the flash loan, he left with a profit of 6,106 WETH.
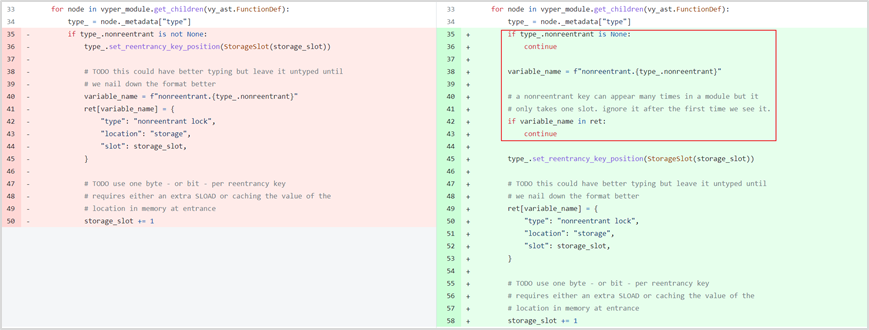
Vulnerability analysis: This attack is a typical reentrancy attack. After decompiling the bytecode of the attacked project contract, we can find from the figure below that the two functions add_liquidity and remove_liquidity verify different storage slots when verifying the storage slot value. Using different storage slots, the reentrancy lock may fail. At this point, it is suspected that there is a vulnerability in the underlying design of Vyper.
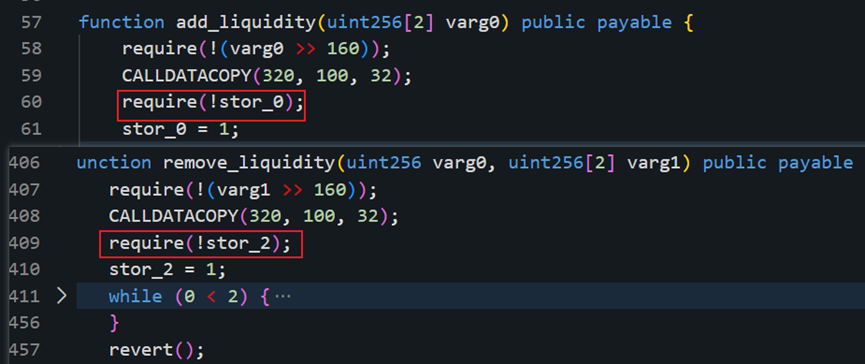
Combined with what Curve official tweeted. In the end, it was located as a Vyper version vulnerability. The vulnerability exists in versions 0.2.15, 0.2.16, and 0.3.0, and there is a defect in the reentrant lock design. We compared the 0.2.14 before 0.2.15 and the 0.3.1 after 0.3.0, and found that this part of the code is constantly being updated. The old 0.2.14 and the newer 0.3.1 versions do not have this problem.
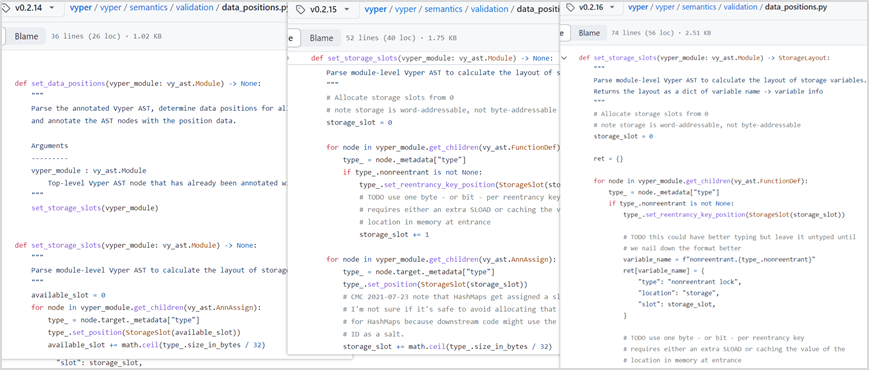
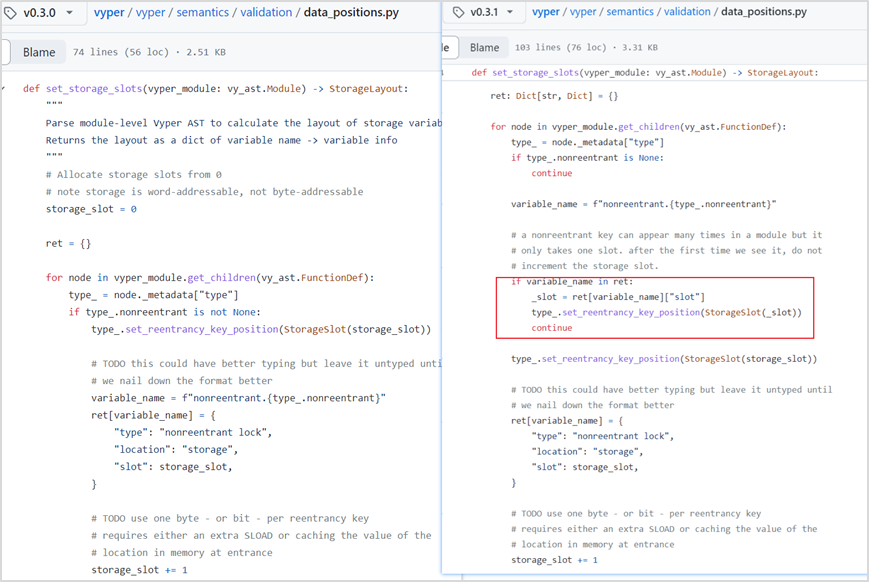
In the Vyper corresponding reentrant lock related settings file data_positions.py, the value of storage_slot will be overwritten. In ret, the first lock slot is 0, and then the next time the function is called, the lock slot will be increased by 1, and the reentrant lock will be invalid.
2. Phishing Attacks
Phishing is a cyberattack that aims to obtain sensitive information or induce malicious actions by deceiving and inducing the target. This attack is usually carried out through email, social media, text messages or other communication channels. The attacker will pretend to be a trusted entity, such as a project owner, an authority, a KOL, etc., to lure the victim to provide private keys, mnemonics or transaction authorization. Similar to contract vulnerability attacks, phishing attacks were high in incidence and high in losses in Q3, with a total of 107 phishing attacks, of which 58 occurred in July.
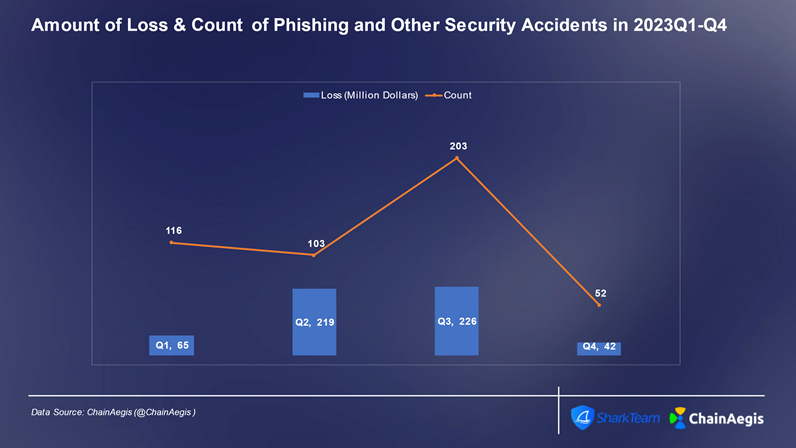
Figure: Web 3 2023 Number of phishing attacks and loss amount per quarter (million USD)
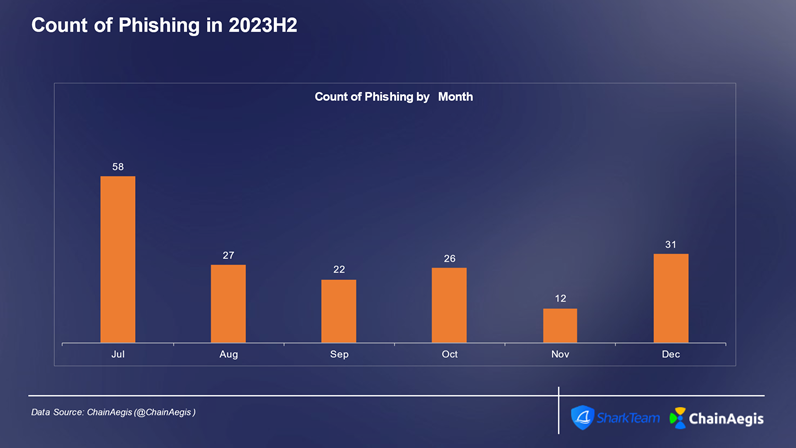
Figure: Number of phishing attacks per month in Web 3 2023
Analysis of asset transfer on a typical phishing attack chain
On September 7, 2023, the address (0x13e382) suffered a phishing attack, resulting in a loss of more than $24 million.stealThrough withdrawal, fund exchange and decentralized fund transfer, 3,800 ETH of the lost funds were transferred to Tornado.Cash in batches, 10,000 ETH were transferred to the intermediate address (0x702350), and 1078,087 DAI It remains at the middle address (0x4F2F02) so far.
This is a typical phishing attack. The attacker deceiveswallet授权或私钥,窃取用户资产,已形成了以钓鱼 + 洗钱的黑色产业链,目前越来越多的诈骗团伙甚至是国家黑客都采用钓鱼的方式在 Web3 领域为非作歹,非常需要大家关注和警惕。
Based on the tracking and analysis of SharkTeam's on-chain big data analysis platform ChainAegis (https://app.chainaegis.com/), we will conduct relevant analysis on the fraud process, fund transfer and on-chain behavior of typical phishing attacks.
(1) Phishing attack process
The victim address (0x13e382) authorized rETH and stETH to the scammer address 1 (0x4c10a4) via 'Increase Allowance'.

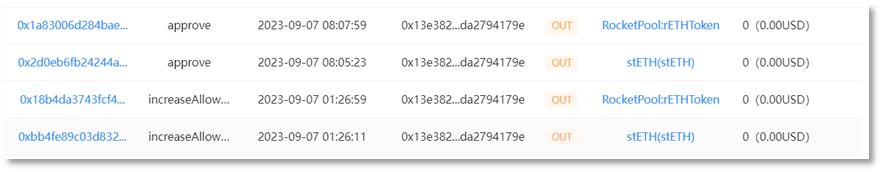
Scammer address 1 (0x4c10a4) transferred 9,579 stETH from the victim address (0x13e382) to scammer address 2 (0x693b72), with an amount of approximately US$15.32 million.
Scammer address 1 (0x4c10a4) transferred 4,850 rETH from the victim address (0x13e382) to scammer address 2 (0x693b72), with an amount of approximately US$8.41 million.
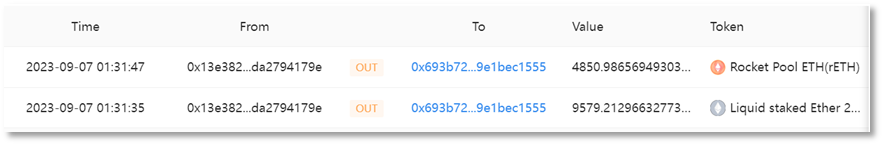
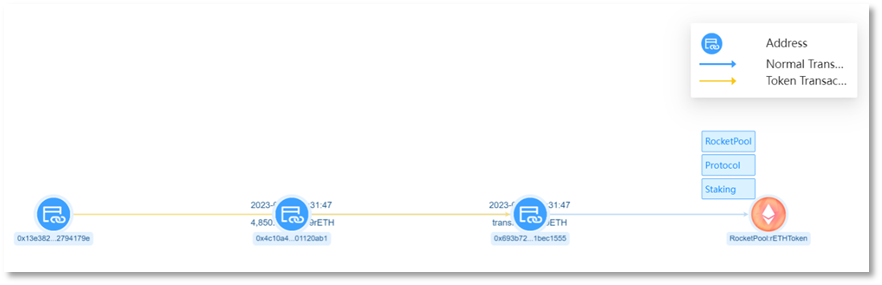
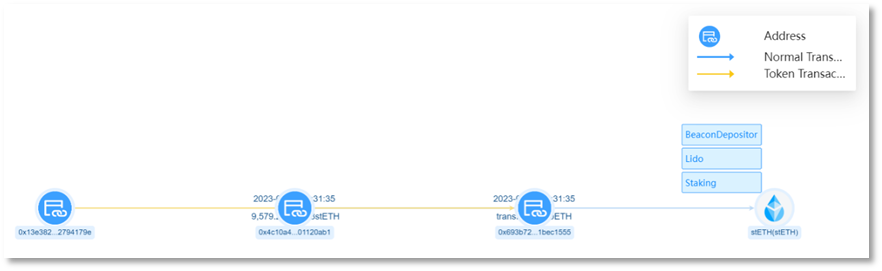
(2) Asset exchange and transfer
Convert the stolen stETH and rETH into ETH. Since the early morning of 2023-09-07, the scammer address 2 (0x693b72) has conducted multiple conversion transactions on UniswapV2, UniswapV3, and Curve platforms, converting all 9,579 stETH and 4,850 rETH into ETH, with a total of 14,783.9413 ETH.
stETH exchange:
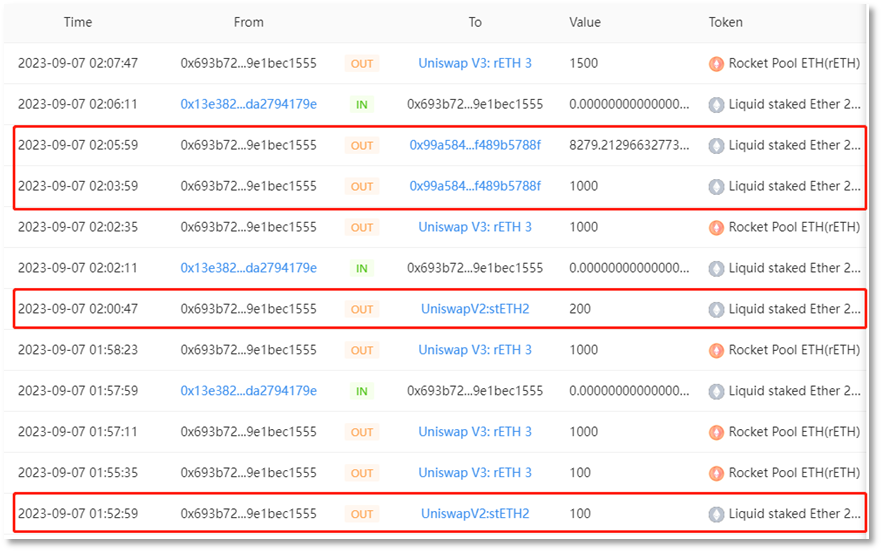
rETH exchange:

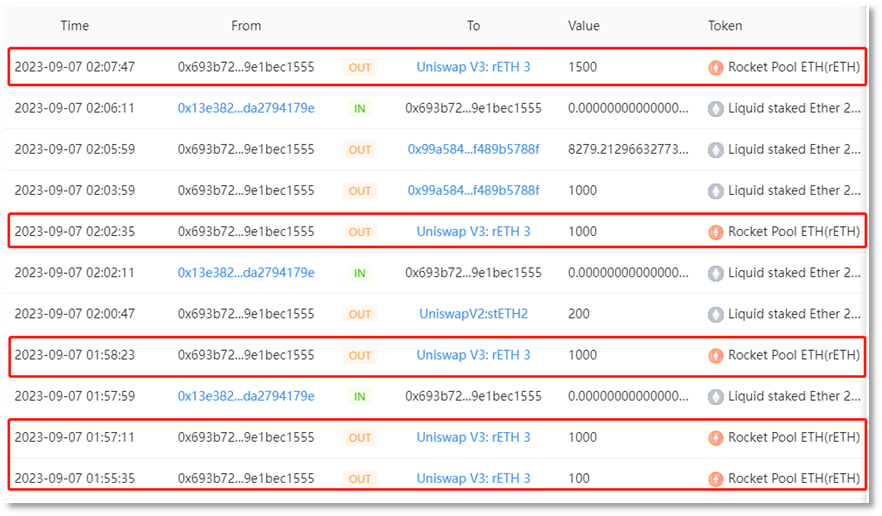
Part of ETH is converted into DAI。诈骗者地址 2(0x693b72)将 1,000ETH 通过 UniswapV3 平台兑换成 1,635,047.761675421713685327 DAI。诈骗者通过分散式资金转移手段,将盗用资金转移至多个中间钱包地址,合计 1,635,139 DAI 和 13,785 ETH。其中 1,785 ETH 被转移至中间地址(0x4F2F02),2,000 ETH 被转移至中间地址(0x2ABdC2)以及 10,000 ETH 被转移至中间地址(0x702350)。此外,中间地址(0x4F2F02)于次日获得 1,635,139 DAI
中间钱包地址(0x4F2F02)资金转移:
This address has 1,785 ETH and 1,635,139 DAI through a layer of fund transfer. Dispersed transfer of funds DAI, and small amounts converted to ETH
First, the scammers began to transfer 529,000 DAI through 10 transactions in the early morning of September 7, 2023. Subsequently, the first 7 transactions totaling 452,000 DAI were transferred from the intermediate address to 0x4E5B2e (FixedFloat), the 8th transaction was transferred from the intermediate address to 0x6cC5F6 (OKX), and the last 2 transactions totaling 77,000 DAI were transferred from the intermediate address to 0xf1dA17 (eXch).
Secondly, on September 10, 28,052 DAI was exchanged for 17.3 ETH via UniswapV2.
From September 8th to September 11th, 18 transactions were carried out to transfer all 1,800 ETH to Tornado.Cash.
After the transfer, the address still had 1,078,087 DAI of stolen funds left.
Funds transfer to the intermediate address (0x2ABdC2):
This address has 2,000 ETH after a layer of fund transfer. First, the address transferred 2,000 ETH to the intermediate address (0x71C848) on September 11.
Subsequently, the intermediate address (0x71C848) transferred funds twice on September 11 and October 1, totaling 20 transactions, with each transaction transferring 100 ETH, for a total of 2,000 ETH to Tornado.Cash.
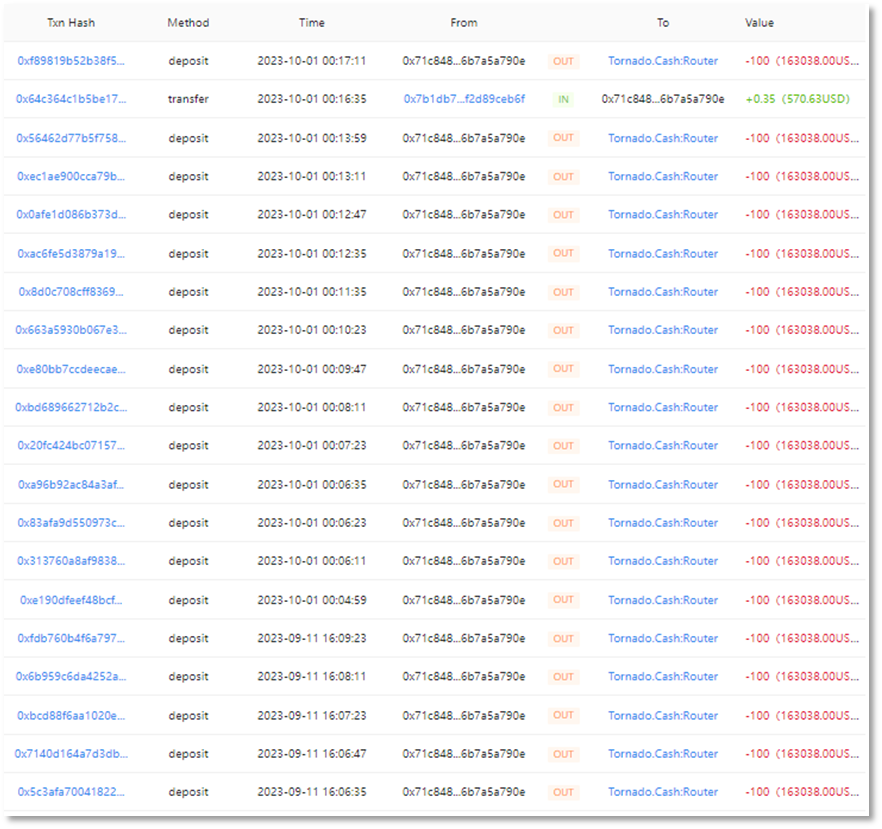
This address has 10,000 ETH after a layer of fund transfer. As of October 08, 2023, 10,000 ETH is still in the account of this address and has not been transferred.
地址线索追踪:经过对诈骗者地址 1(0x4c10a4)和诈骗者地址 2(0x693b72)的历史交易进行分析,发现曾有一个 EOA 地址(0x846317)转账 1.353 ETH 至诈骗者地址 2(0x693b72),而该 EOA 地址资金来源涉及与中心化交易所 KuCoin 和 Binance 的热钱包地址。
3. Rugpull and Fraud
The frequency of Rugpull fraud incidents in 2023 showed a significant upward trend, reaching 73 in Q4, with a loss of US$19 million and an average single loss of approximately US$26,000. The quarter with the highest proportion of Rugpull fraud losses throughout the year was Q2, followed by Q3, with loss proportions of more than 30%.
In the second half of 2023, there were 139 Rugpull incidents and 12 fraud incidents, resulting in losses of $71.55 million and $340 million, respectively.
In the second half of 2023, Rugpull incidents mainly occurred on BNBChain, reaching 91 times, accounting for more than 65%, with a loss of 29.57 million US dollars, accounting for 41%. Ethereum (44 times) was second, with a loss of 7.39 million US dollars. In addition to Ethereum and BNBChain, the BALD Rugpull incident occurred on the Base chain in August, causing serious losses, with a loss of 25.6 million US dollars.
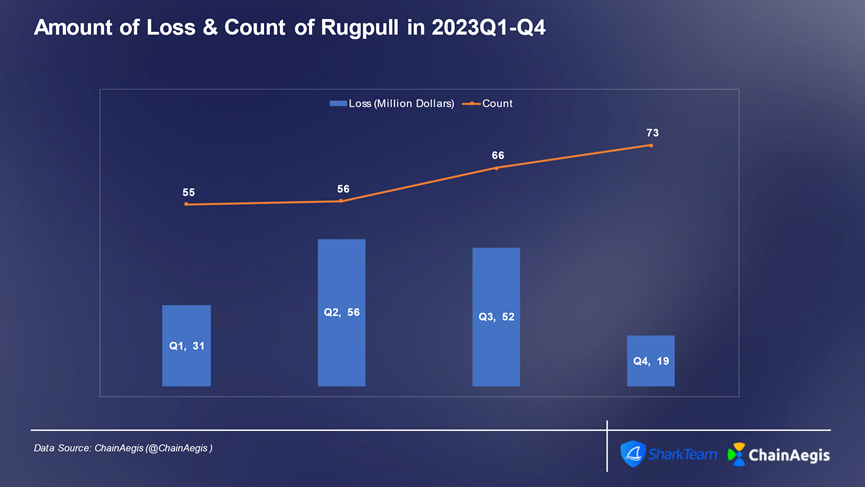
Figure: Number of Rugpull and Scam incidents and loss amount per quarter in Web 3 2023 (million USD)
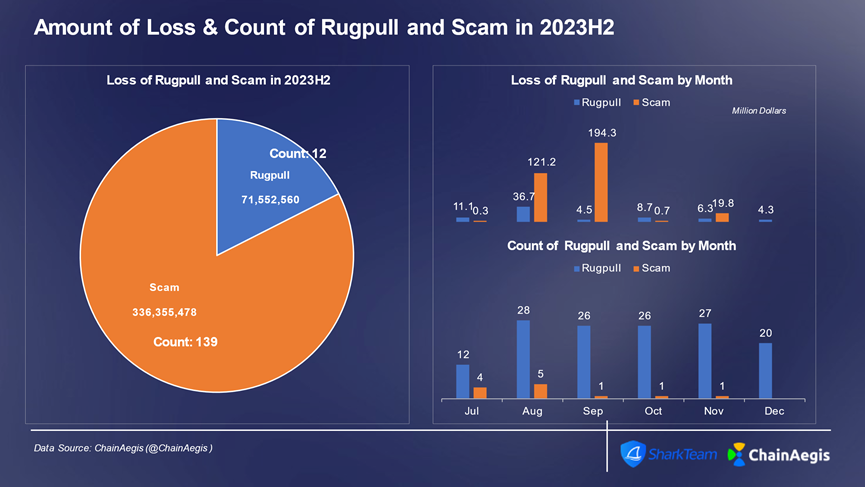
Figure: Number of Rugpull and Scam incidents and loss amount in Web 3 2023H2 per month
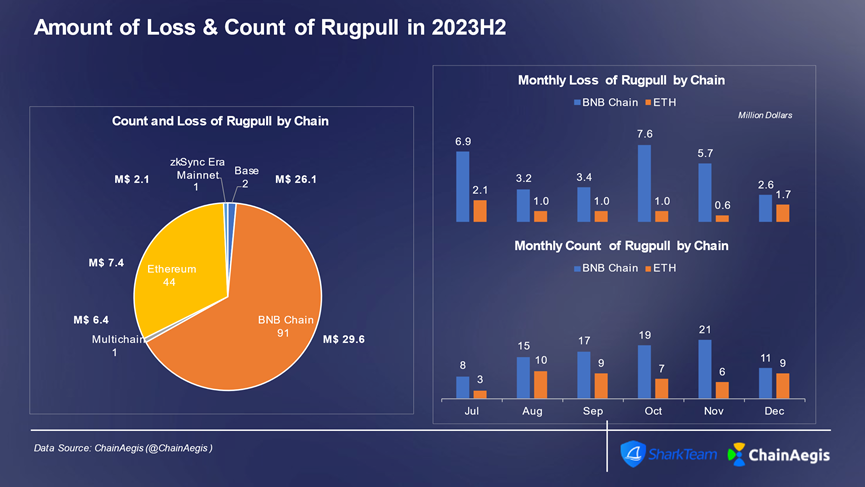
Figure: Number of Rugpull events and loss amounts on different chains per month in Web 3 2023H2
Rugpull fraud factory behavior analysis
A Rug fraud factory model is popular on BNBChain, which is used to mass-produce Rugpull Token并进行欺诈。让我们一起看看假 SEI、X、TIP 和 Blue 几个代币的 Rugpull 工厂欺诈行为模式。
(1) SEI
First, the fake SEI token owner 0x0a8310eca430beb13a8d1b42a03b3521326e4a58 redeemed 249 fake SEIs at a price of 1U.
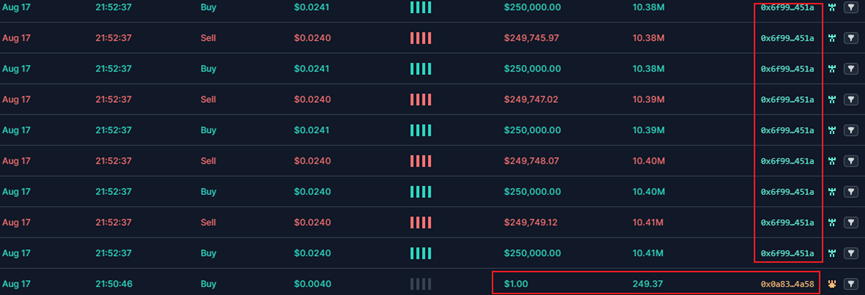
Then, 0x6f9963448071b88FB23Fd9971d24A87e5244451A performed batch buy and sell operations. Under the buy and sell operations, the liquidity of the token increased significantly and the price also rose.
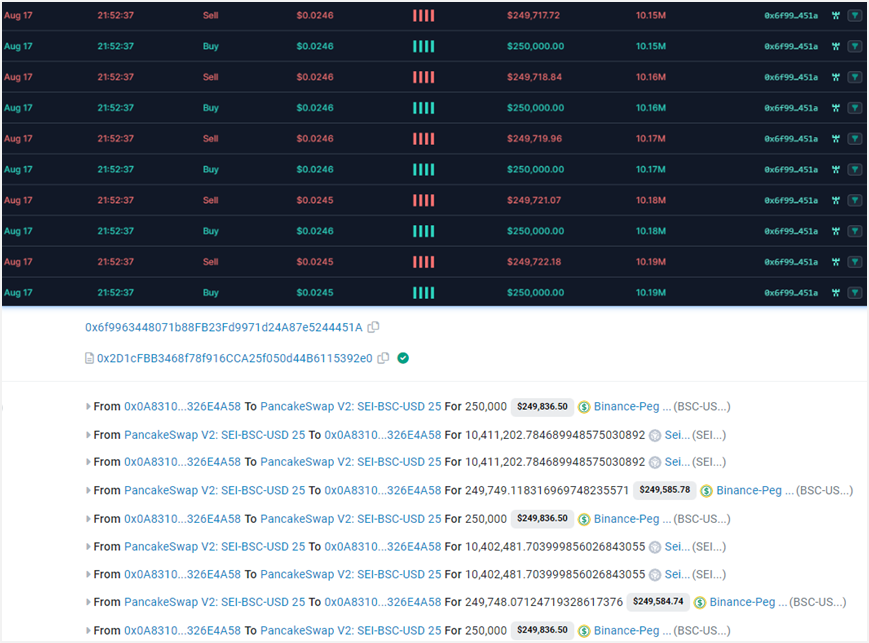
Through phishing and other means of publicity, a large number of users are lured to buy, and as liquidity increases, the token price doubles.
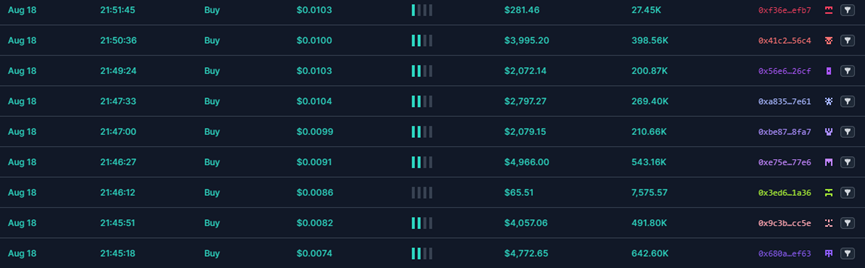
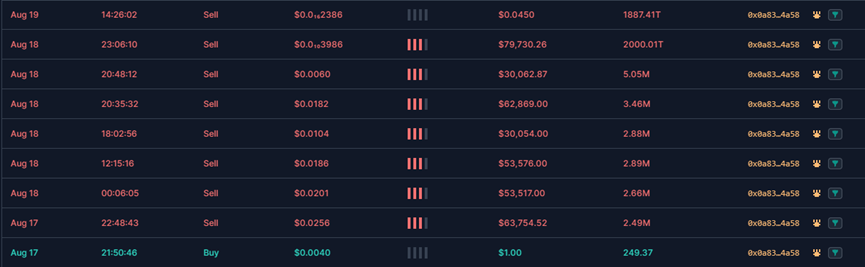
When the price of a token reaches a certain value, the token owner enters the market to sell and perform Rugpull. As can be seen from the figure below, the entry and harvesting time periods and prices are different.
(2) Fake X, fake TIP, fake Blue
First, X, TIP and Blue token owners 0x44A028Dae3680697795A8d50960c8C155cBc0D74 exchanged 1U for the corresponding tokens. Then, the same as the fake Sei tokens.
0x6f9963448071b88FB23Fd9971d24A87e5244451A Batch buy and sell operations. Under the buy and sell operations, liquidity increased significantly and prices rose.
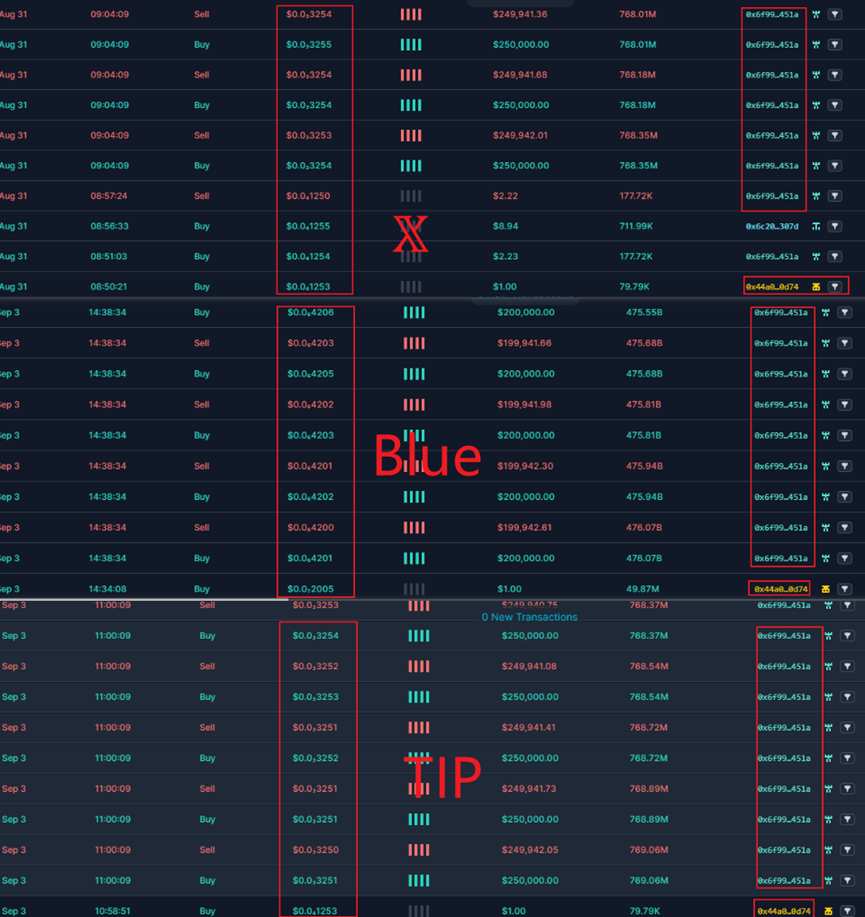
Then, through phishing and other means, they promote the product and entice a large number of users to buy it. As liquidity increases, the token price doubles.
Just like the fake SEI, when the token price reaches a certain value, the token owner enters the market to sell and perform Rugpull. As can be seen from the figure below, the entry and harvesting time periods and prices are different.
The fluctuation charts of fake SEI, fake X, fake TIP and fake Blue tokens are as follows:
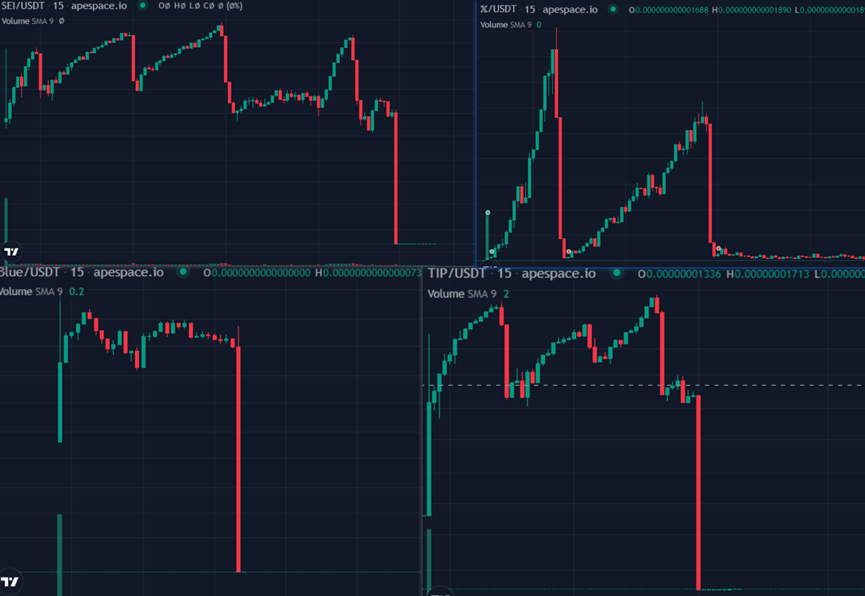
We can learn from the source of funds and behavior patterns:
In the fund tracing content, the funds of the creators of the token factory and the token creators came from multiple EOA accounts. There were also fund transfers between different accounts, some of which were transferred through phishing addresses, some were obtained through previous token Rugpull behaviors, and some were obtained through mixing platforms such as Tornado Cash. The use of multiple methods to transfer funds is intended to build a complex and intricate fund network. Multiple token factory contracts were also created at different addresses, and tokens were produced in large quantities.
When analyzing the token Rugpull behavior, we found that the address
0x6f9963448071b88FB23Fd9971d24A87e5244451A is one of the sources of funds. When manipulating the token price, a batch method is also used. The address 0x072e9A13791f3a45fc6eB6AD38e6ea258C080cc3 also acts as a fund provider, providing corresponding funds to multiple token holders.
Through analysis, it can be found that behind this series of behaviors there is a Web3 fraud gang with a clear division of labor, which constitutes a black industry chain, mainly involving hot spot collection, automatic coin issuance, automatic trading, false propaganda, phishing attacks, Rugpull harvesting and other links, which mostly occur in BNBChain. The issued Rugpull fake tokens are closely related to industry hot events, and are highly confusing and inciting. Users need to be vigilant at all times, stay rational, and avoid unnecessary losses.
Ransomware
In 2023, the threat of ransomware attacks still threatens organizations and enterprises at all times. Ransomware attacks are becoming more and more sophisticated, and attackers use various techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in organizational systems and networks. The ever-spreading ransomware attacks continue to pose a major threat to corporate organizations, individuals, and critical infrastructure around the world. Attackers are constantly adjusting and improving their attack strategies, using leaked source code, intelligent attack schemes, and emerging programming languages to maximize their illegal gains.
LockBit, ALPHV/BlackCat and BlackBasta are the most active ransomware extortion groups.
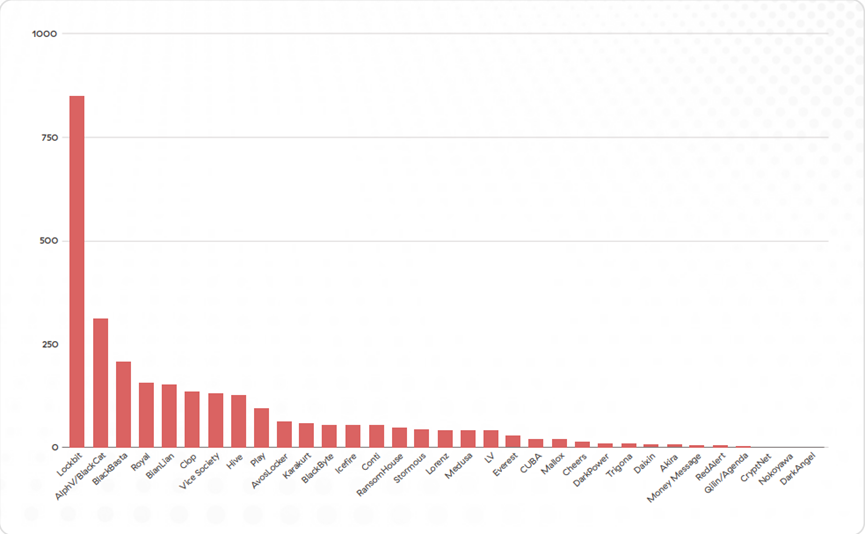
Figure: Number of victims of ransomware organizations
目前,越来越多的勒索软件采取通过加密货币收款的方式,以 Lockbit 为例,最近被 LockBit 攻击的企业有:今年 6 月底台积电、10 月波音公司、11 月中国工商银行美国全资子公司等等,大多采用比特币收取赎金,并且 LockBit 收到赎金后会进行加密货币洗钱,下面我们以 Lockbit 为例对勒索软件洗钱模式进行分析。
根据 ChainAegis 分析,LockBit 勒索软件大多采用 BTC 收取赎金,使用不同收款地址,部分地址和收款金额整理如下,单笔勒索的 BTXiaobai NavigationC 在 0.07 个到 5.8 个不等,约 2,551 美元到 211,311 美元不等。
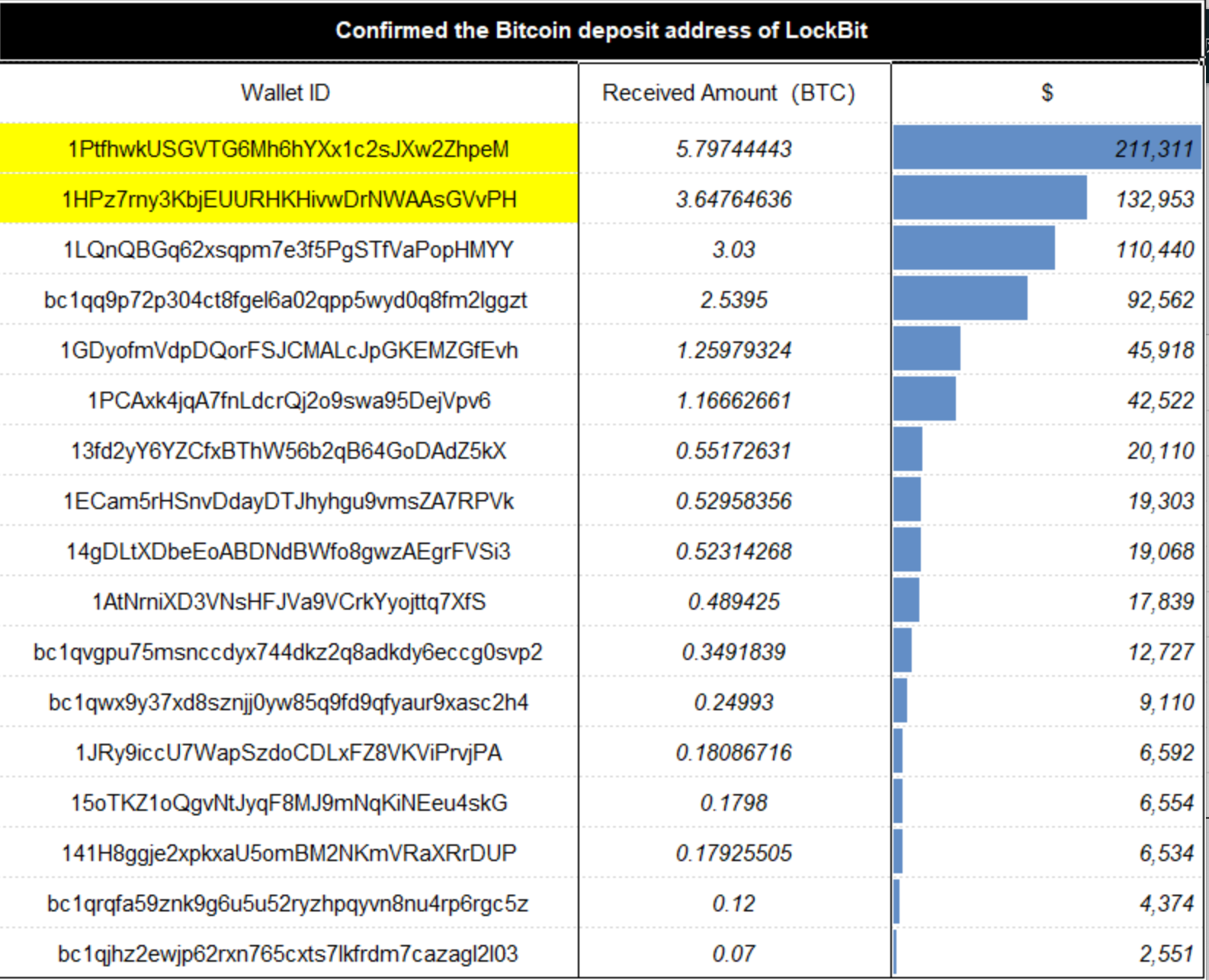
Figure: Some of LockBit’s payment addresses and amounts
The two addresses with the highest amount of funds involved are used for on-chain address tracking and anti-money laundering analysis:
Ransom payment address 1: 1PtfhwkUSGVTG6Mh6hYXx1c2sJXw2ZhpeM;
Ransom payment address 2: 1HPz7rny3KbjEUURHKHivwDrNWAAsGVvPH.
(1) Ransom payment address 1: 1PtfhwkUSGVTG6Mh6hYXx1c2sJXw2ZhpeM
According to the analysis in the figure below, address 1 (1Ptfhw) received a total of 17 on-chain transactions from March 25, 2021 to May 15, 2021. After receiving the funds, the assets were quickly transferred to 13 core intermediate addresses. These intermediate addresses were transferred to 6 second-layer intermediate addresses through funds, namely: 3FVzPX…cUvH, 1GVKmU…Bbs1, bc1qdse…ylky, 1GUcCi…vSGb, bc1qan…0ac4 and 13CPvF…Lpdp.
The intermediate address 3FVzPX…cUvH, through on-chain analysis, was found to eventually flow to the dark web address 361AkMKNNWYwZRsCE8pPNmoh5aQf4V7g4p.
The middle address 13CPvF…Lpdp transferred a small amount of 0.00022 BTC to CoinPayments. There were 500 similar transactions, and a total of 0.21 BTC were all collected to the CoinPayments address: bc1q3y…7y88, using CoinPayments for money laundering.
其他中间地址最终流入中心化交易所币安和 Bitfinex。
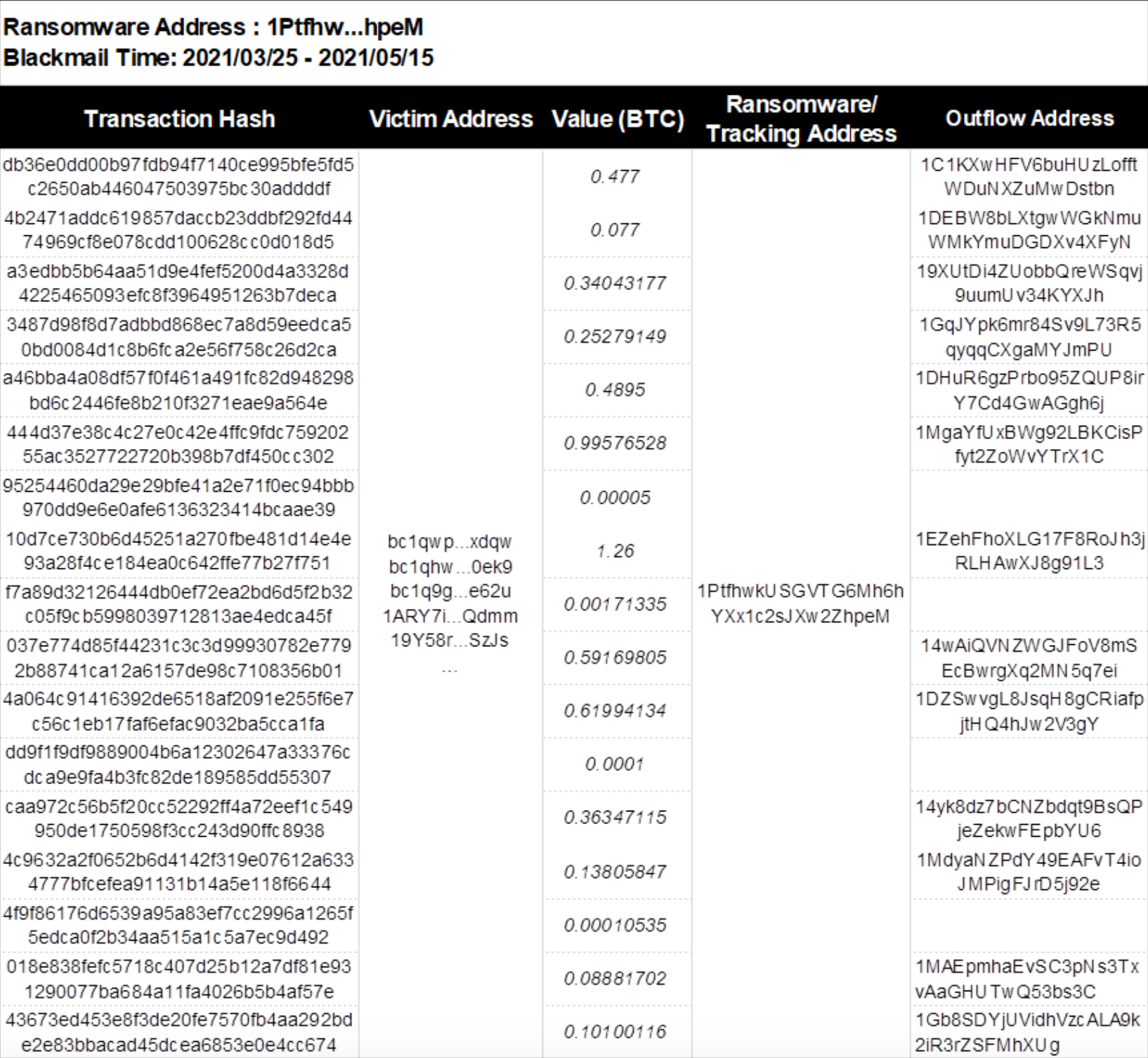
Figure: Details of source and outflow of funds for address 1 (1Ptfhw…hpeM)
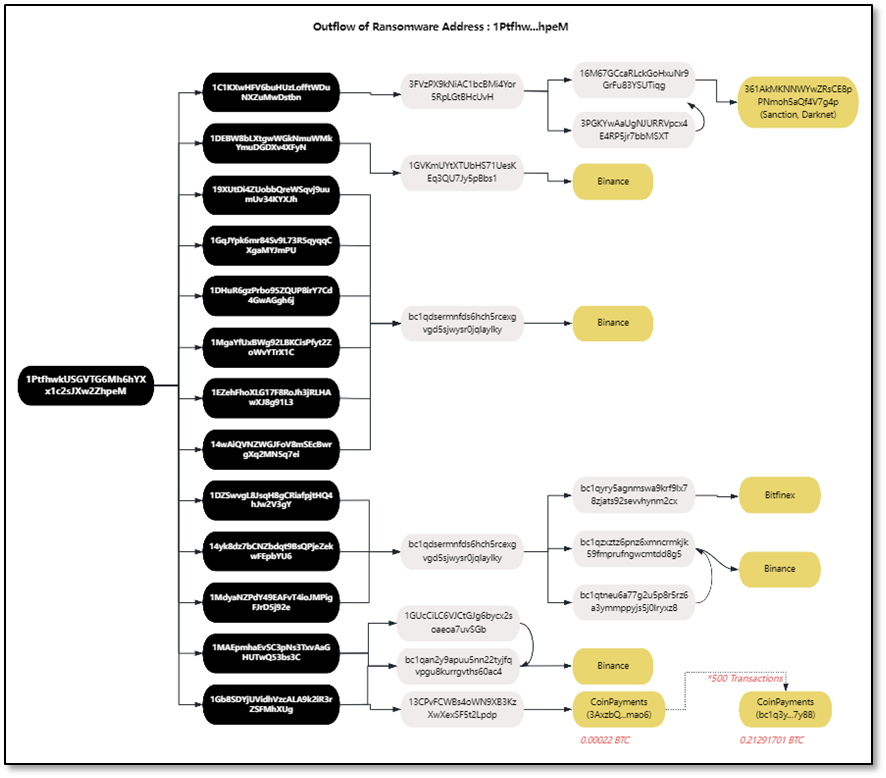
Figure: Fund flow tracking of address 1 (1Ptfhw…hpeM)
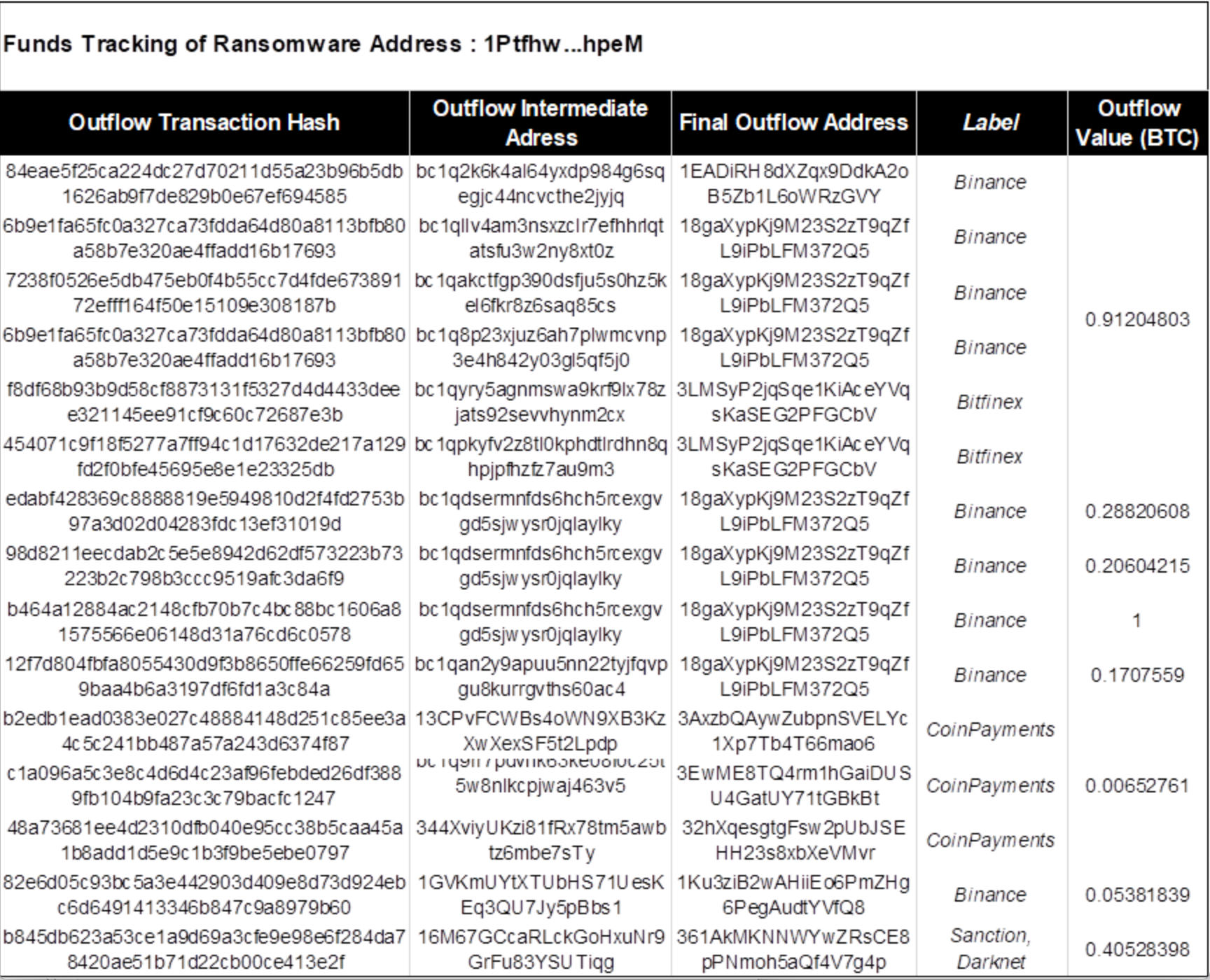
Figure: Intermediate addresses and fund flow details involved in address 1 (1Ptfhw…hpeM)
Figure: Transaction map of address 1 (1Ptfhw…hpeM)
(2) Ransom payment address 2: 1HPz7rny3KbjEUURHKHivwDrNWAAsGVvPH
The victim paid 4.16 BTC to the ransom operator LockBit through 11 transactions between May 24, 2021 and May 28, 2021. Immediately, address 2 (1HPz7rn…VvPH) quickly transferred 1.89 BTC of the ransom funds to intermediate address 1: bc1qan…0ac4, 1.84 to intermediate address 2: 112QJQj…Sdha, and 0.34 to intermediate address 3: 19Uxbt…9RdF.
最终中间地址 2: 112QJQj…Sdha 和中间地址 3: 19Uxbt…9RdF 均将资金转到中间地址 1: bc1qan…0ac4。紧接着,中间地址 1 bc1qan…0ac4 继续资金转移,一小部分资金直接转入币安交易所,另外一部分资金通过中间地址层层转移,最终转移至币安和其他平台进行洗钱,具体交易明细和地址标签如下。
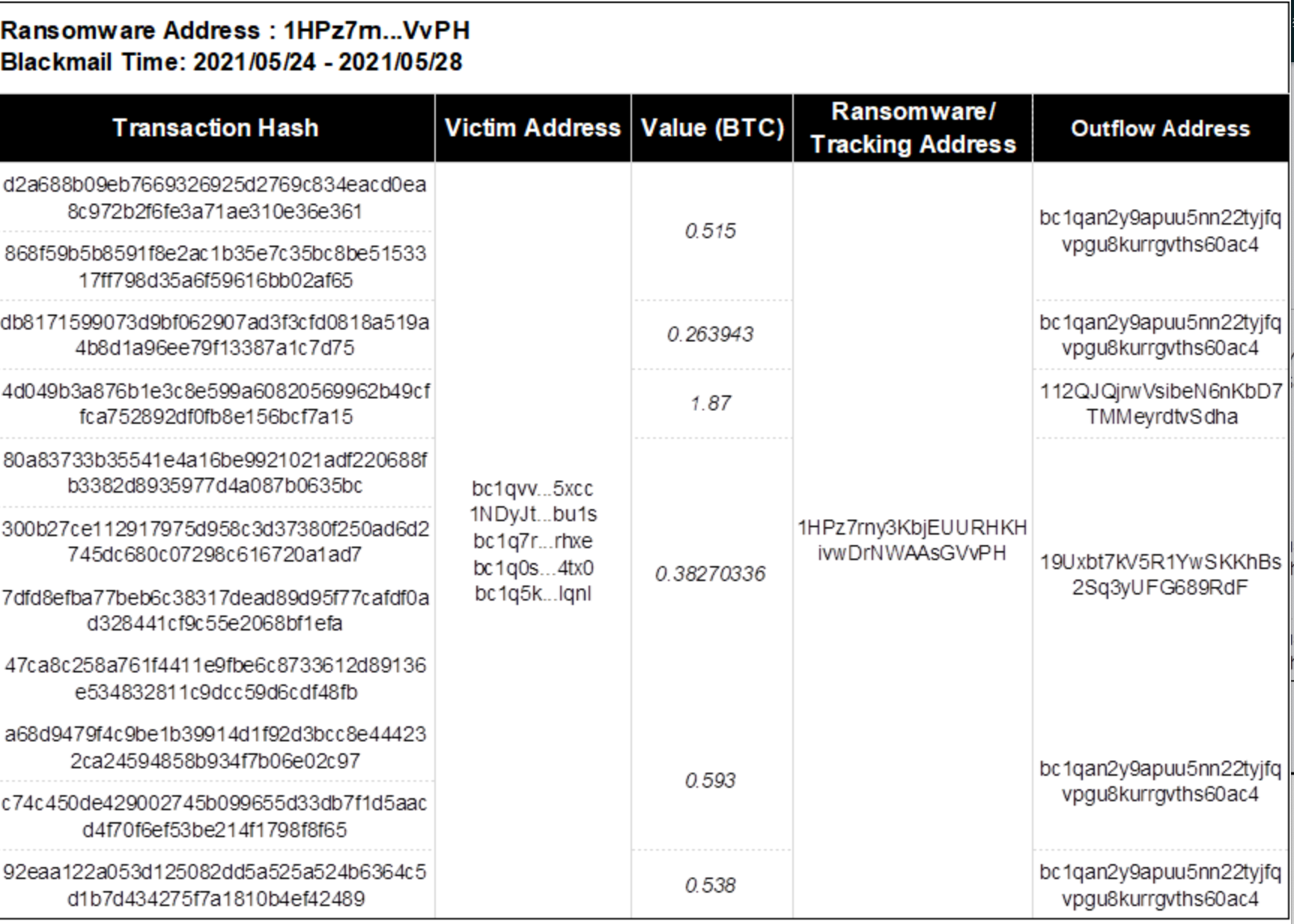
Figure: Details of source and outflow of funds from address 2 (1HPz7rn…VvPH)
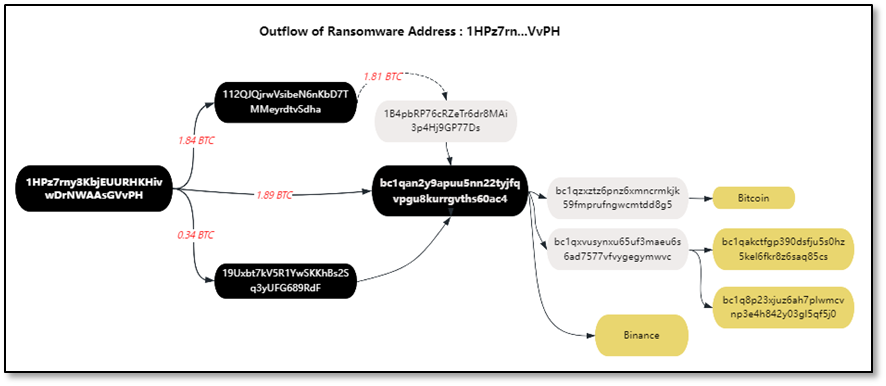
Figure: Address 2 (1HPz7rn…VvPH) fund flow tracking

Figure: Intermediate addresses and fund flow details involved in address 2 (1HPz7rn…VvPH)
After receiving the ransom, LockBit will launder the money through cryptocurrency. This money laundering model is different from traditional money laundering methods and usually occurs inBlockchainIn terms of cryptocurrency regulation and fund tracking, it is necessary to build on-chain and off-chain analysis and evidence collection capabilities, and on the other hand, to carry out APT-level security attacks and defenses at the network security level, and to have the ability to integrate attack and defense.
5. Money Laundering
Money laundering is an act of legalizing illegal income, which mainly refers to disguising and concealing the source and nature of illegal income and the proceeds generated by it through various means to make it legal in form. Its behavior includes but is not limited to providing fund accounts, assisting in converting property forms, assisting in transferring funds or remitting them abroad. Cryptocurrencies, especially stablecoins, have been used for money laundering activities at a very early time due to their low transfer costs, de-geographical characteristics, and certain anti-censorship characteristics. This is also one of the main reasons why cryptocurrencies have been criticized.
Traditional money laundering activities often use the over-the-counter cryptocurrency market to exchange fiat currency for cryptocurrency or from cryptocurrency to fiat currency. The money laundering scenarios are different and the forms are diverse, but no matter what, the essence of such behavior is to block law enforcement officers' investigation of the funding chain, including traditional financial institution accounts or crypto institution accounts.
Unlike traditional money laundering activities, the new type of cryptocurrency money laundering activities targets the cryptocurrency itself. The crypto industry infrastructure including wallets, cross-chain bridges, decentralized trading platforms, etc. will be illegally used.
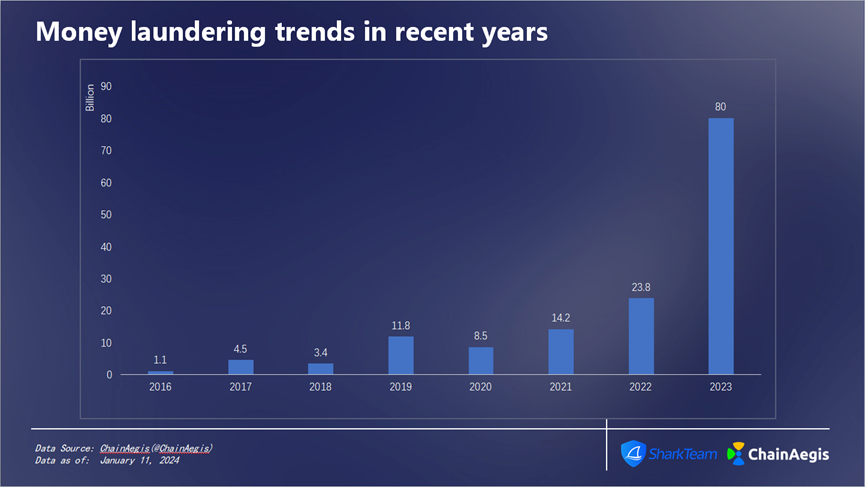
Figure: Money laundering amount in recent years
From 2016 to 2023, the total amount of money laundering in cryptocurrency reached 147.7 billion US dollars. Starting from 2020, the amount of money laundering has been increasing at a rate of 67% per year, reaching 23.8 billion US dollars in 2022 and 80 billion US dollars in 2023. The amount of money laundering is staggering, and cryptocurrency anti-money laundering actions are imperative.
According to statistics from the ChainAegis platform, the amount of funds in the on-chain currency mixing platform Tornado Cash has maintained rapid growth since January 2020. Currently, there are nearly 3.62 million ETH deposits in this fund pool, with a total deposit of US$7.8 billion. Tornado Cash has become the largest money laundering center in Ethereum. However, with the US law enforcement agencies issuing sanctions on Tornado Cash in August 2022, Tornado Cash's weekly deposits and withdrawals have fallen exponentially, but because of the decentralized nature of Tornado Cash, it cannot be stopped at the source, and funds are still pouring into the system for currency mixing.
Analysis of Lazarus Group (North Korean APT organization) money laundering model
A state-level APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) organization is a top hacker group with state-backed backgrounds, specializing in long-term and persistent cyber attacks against specific targets. The North Korean APT organization Lazarus Group is a very active APT group. Its main purpose of attack is to steal funds. It is the biggest threat to financial institutions around the world. In recent years, many attacks and fund theft cases in the field of cryptocurrency were caused by them.
The security incidents and losses in the field of encryption caused by Lazarus attacks that have been clearly counted are as follows:
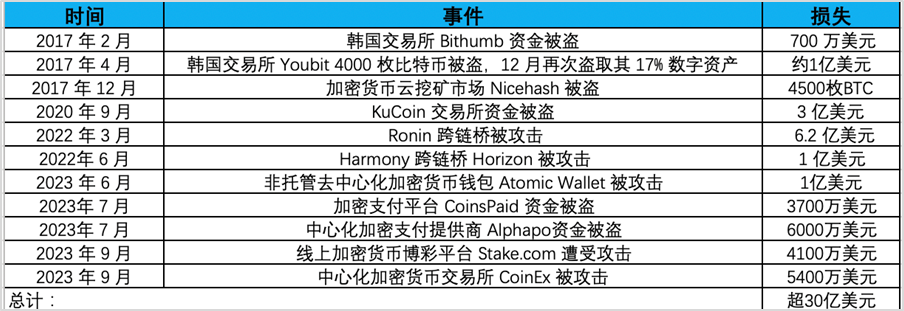
More than $3 billion was stolen by Lazarus in cyberattacks. It is reported that the Lazarus hacker group is backed by North Korea's strategic interests and provides funding for North Korea's nuclear and ballistic missile programs. For this reason, the United States announced a reward of $5 million to sanction the Lazarus hacker group. The U.S. Treasury Department has also added the relevant addresses to the OFAC Specially Designated Nationals (SDN) list, prohibiting U.S. individuals, entities and related addresses from trading to ensure that state-sponsored groups cannot cash out these funds, thereby imposing sanctions. Ethereum developer Virgil Griffith was sentenced to five years and three months in prison for helping North Korea use virtual currency to evade sanctions. In 2023, OFAC also sanctioned three people related to the Lazarus Group. Two of the sanctioned persons, Cheng Hung Man and Wu Huihui, were over-the-counter (OTC) traders who facilitated cryptocurrency transactions for Lazarus, while the third person, Sim Hyon Sop, provided other financial support.
Despite this, Lazarus has completed the transfer and laundering of more than $1 billion in assets. Their money laundering model is analyzed as follows. Taking the Atomic Wallet incident as an example, after removing the technical interference factors set by the hacker (a large number of fake token transfer transactions + multi-address split accounts), the hacker's fund transfer model can be obtained:
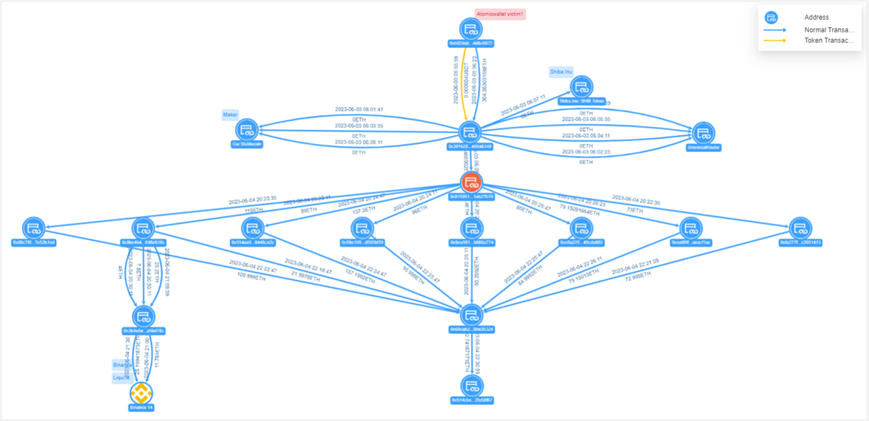
Figure: Atomic Wallet victim 1 fund transfer view
Victim 1's address 0xb02d...c6072 transferred 304.36 ETH to the hacker's address 0x3916...6340, which was split 8 times through the intermediate address 0x0159...7b70 and then collected at the address 0x69ca...5324. The collected funds were then transferred to the address 0x514c...58f67, where the funds are still currently, with a balance of 692.74 ETH (worth $1.27 million).
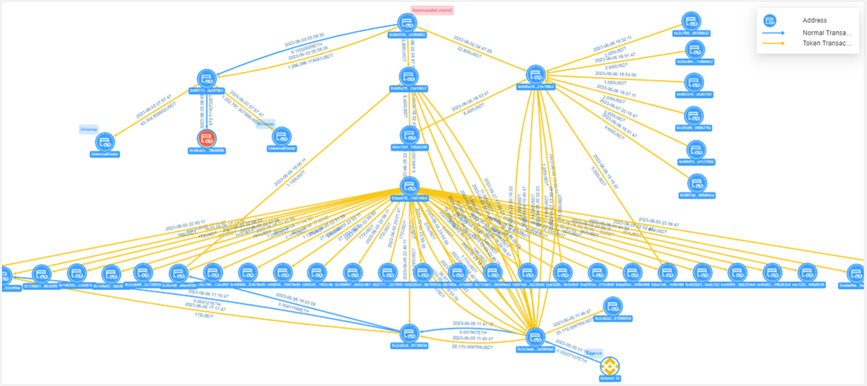
Figure: Atomic Wallet victim 2 fund transfer view
Victim 2's address 0x0b45…d662 transferred 1.266 million USDT to the hacker's address 0xf0f7…79b3, and the hacker divided it into three transactions, two of which were transferred to Uniswap with a total transfer amount of 1.266 million USDT; the other was transferred to the address 0x49ce…80fb with a transfer amount of 672.71 ETH. Victim 2 transferred 22,000 USDT to the hacker's address 0x0d5a…08c2, and the hacker split the account multiple times through the intermediate address 0xec13…02d6, etc., and directly or indirectly collected the funds to the address 0x3c2e…94a8.
This money laundering model is highly consistent with the money laundering model in the previous Ronin Network and Harmony attacks, both of which include three steps:
(1) Stolen funds sorting and exchange: After launching the attack, the original stolen tokens are sorted out, and multiple tokens are swapped into ETH through dex and other methods. This is a common way to circumvent fund freezes.
(2) Stolen funds collection: The sorted ETH is collected into several one-time wallet addresses. In the Ronin incident, the hacker used a total of 9 such addresses, Harmony used 14, and the Atomic Wallet incident used nearly 30 addresses.
(3) Transfer of stolen funds: Use the collection address to launder the money through Tornado.Cash. This completes the entire fund transfer process.
In addition to the same money laundering steps, there is also a high degree of consistency in the details of money laundering:
(1) The attackers were very patient and spent up to a week laundering money, and began subsequent money laundering operations a few days after the incident.
(2) Automated transactions are used in the money laundering process. Most fund collection operations involve a large number of transactions with small time intervals and a uniform pattern.
Through analysis, we believe that Lazarus' money laundering model is usually as follows:
(1) Multiple accounts and multiple small transfers of assets increase the difficulty of tracking.
(2) Start to create a large number of counterfeit currency transactions to increase the difficulty of tracking. Taking the Atomic Wallet incident as an example, 23 of the 27 intermediate addresses were counterfeit currency transfer addresses. In the recent analysis of the Stake.com incident, similar technology was also found. However, the previous Ronin Network and Harmony incidents did not have this interference technology, indicating that Lazarus' money laundering technology is also upgrading.
(3) More on-chain methods (such as Tonado Cash) are used for coin mixing. In early incidents, Lazarus often used centralized exchanges to obtain start-up funds or conduct subsequent OTC. However, in recent years, centralized exchanges have been used less and less. It can even be considered that they are trying to avoid using centralized exchanges as much as possible. This may be related to several recent sanctions incidents.
VI. Sanctions and Supervision
Agencies such as the U.S. Treasury Department’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) and similar agencies in other countries enforce sanctions by targeting countries, regimes, individuals, and entities that are deemed to pose a threat to national security and foreign policy. Traditionally, the enforcement of sanctions has relied on the cooperation of mainstream financial institutions, but some bad actors have turned to cryptocurrencies to circumvent these third-party intermediaries, creating new challenges for policymakers and sanctions authorities. However, the inherent transparency of cryptocurrencies, and the willingness of cryptocurrency services to comply, especially many centralized exchanges that act as a link between cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies, have proven that it is possible to enforce sanctions in the cryptocurrency world.
Here are some of the individuals or entities with ties to cryptocurrency that have been sanctioned in the United States in 2023, and the reasons for the OFAC sanctions.
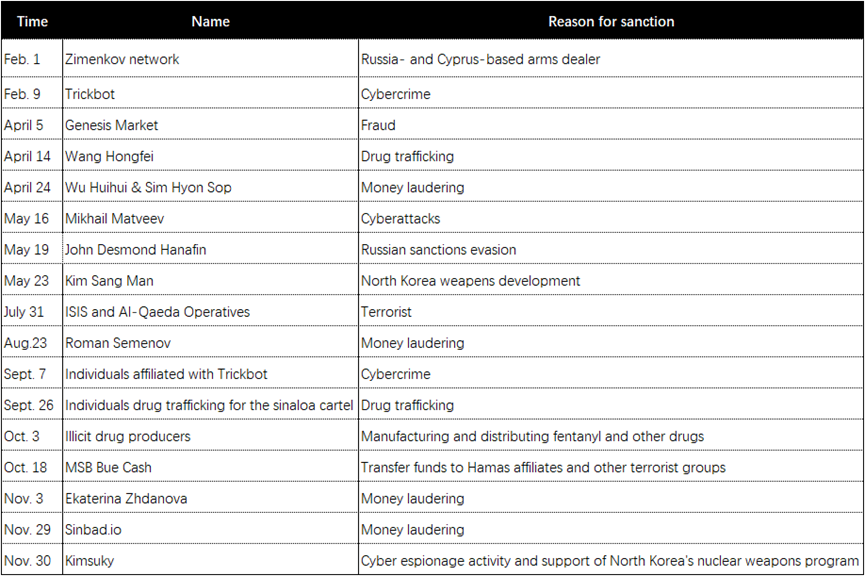
全球最大稳定币背后的公司 Tether 于 2023 年 12 月 9 日宣布,将「冻结」美国外国资产控制办公室 (OFAC) 受制裁个人名单上受制裁个人钱包中的代币。Tether 在其公告中将此举视为自愿步骤,以「主动防止任何潜在的 Tether 代币滥用并加强安全措施」。
This also shows that the investigation and sanctions against cryptocurrency crimes have entered the substantive stage. Core enterprises, in cooperation with law enforcement agencies, can form effective sanctions to supervise and punish cryptocurrency crimes.
In terms of Web3 regulation in 2023, Hong Kong has also made great progress and is sounding the clarion call for "compliant development" of Web3 and the crypto market. When the Monetary Authority of Singapore began to restrict retail customers from using leverage or credit for cryptocurrency transactions in 2022, the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government issued the "Policy Declaration on the Development of Virtual Assets in Hong Kong", and some Web3 talents and companies went to the new promised land.
On June 1, 2023, Hong Kong fulfilled its declaration and issued the "Guidelines for Virtual Asset Trading Platform Operators". The virtual asset trading platform licensing system was officially implemented, and Type 1 (Securities Trading) and Type 7 (Providing Automated Trading Services) licenses have been issued.
Currently, institutions such as OKX, BGE, HKbitEX, HKVAX, VDX, Meex, PantherTrade, VAEX, Accumulus, and DFX Labs are actively applying for virtual asset trading platform licenses (VASP).
Chief Executive John Lee and Financial Secretary Paul Chan have frequently spoken out on behalf of the Hong Kong government to support the establishment of Web3 in Hong Kong and attract crypto companies and talents from all over the world to build it. In terms of policy support, Hong Kong has introduced a licensing system for virtual asset service providers, allowing retail investors to trade cryptocurrencies, launched a tens of millions of dollars Web3 Hub Ecosystem Fund, and plans to invest more than HK$700 million to accelerate the development of the digital economy and promote the development of the virtual asset industry. A special task force for the development of Web3.0 has also been established.
However, while the industry is advancing rapidly, risk events are also coming. The unlicensed crypto exchange JPEX involved more than HK$1 billion, the HOUNAX fraud case involved more than 100 million yuan, and the Hong KongDAO and BitCuped suspected of virtual asset fraud... These malicious incidents have attracted great attention from the Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission and the police. The Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission stated that it will formulate risk assessment criteria for virtual asset cases with the police and exchange information every week.
I believe that in the near future, a more complete regulatory and security system will help Hong Kong. As an important financial hub between the East and the West, Hong Kong is embracing Web3.
The article comes from the Internet:SharkTeam: 2023 Cryptocurrency Crime Analysis Report
相关推荐: Sui DeFi 生态一览:4 个月 TVL 增长 10 倍,Move 系新公链的突破与未来
作为在熊市中发起小白导航的公链新秀,Sui正“猥琐发育”,在公链TVL榜上逐步攀登。 撰文:小白导航 coderworld 比特币冲上44000美元大关,在牛回速归的欢腾气氛中,公链的TVL榜单正悄然间产生些许变化。 作为在熊市中发起的公链新秀,Sui正“猥琐…